Learn all Types of Organic Reactions in Class 12 Chemistry with clear examples — Substitution, Addition, Elimination, and Rearrangement reactions. Easy-to-understand notes for board exams, MDCAT, and NEET preparation.
Welcome to Learn Chemistry by Inam Jazbi!
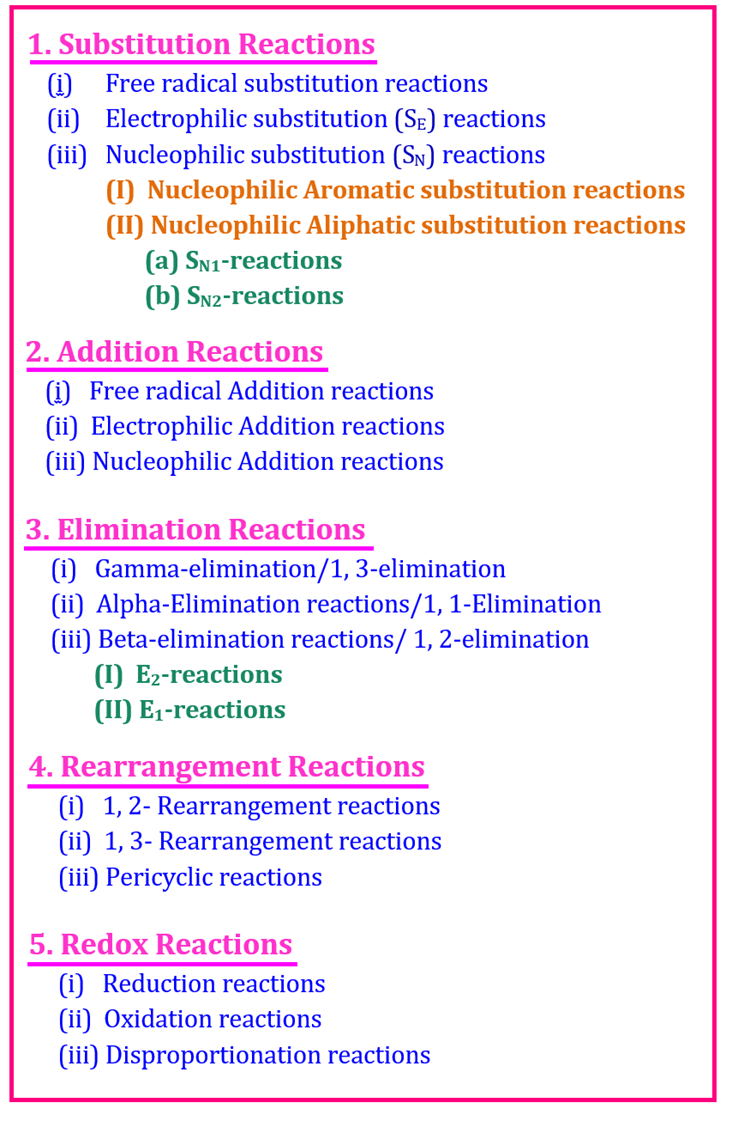
In this article, we’ll discuss one of the most important topics from Class 12 Organic Chemistry — the Types of Organic Reactions. Organic reactions are classified based on how atoms or groups of atoms are replaced, added, removed, or rearranged in molecules.
Understanding these reaction types helps you predict reaction products and mechanisms in board exams and competitive tests like MDCAT and NEET.
Types of organic reactions
Class 12 Chemistry organic reactions
Organic chemistry reaction types
Substitution addition elimination rearrangement reactions
Organic reaction mechanisms
Organic chemistry notes
Organic reactions for board exams
MDCAT Chemistry organic reactions
Class 12 chemistry notes 2025
Organic chemistry chapter 3 notes
🔸 Main Types of Organic Reactions
Organic reactions can be broadly divided into four main types:
| Type of Reaction | Definition | General Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
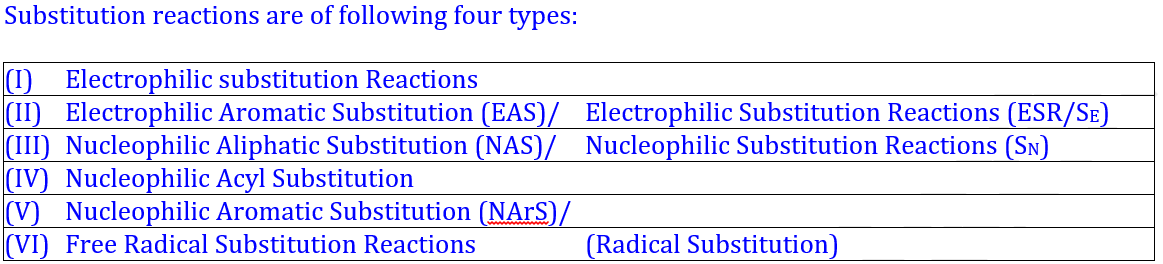
| 1. Substitution Reaction | A reaction in which one atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group. | CH₃Cl + OH⁻ → CH₃OH + Cl⁻ | The Cl atom is substituted by the OH group. |
| 2. Addition Reaction | A reaction in which two or more reactants combine to form a single product (usually occurs in unsaturated compounds like alkenes or alkynes). | C₂H₄ + H₂ → C₂H₆ | Hydrogen adds to the double bond of ethene. |
| 3. Elimination Reaction | A reaction in which a small molecule is removed from a larger molecule, resulting in the formation of a double or triple bond. | C₂H₅Br → C₂H₄ + HBr | Hydrogen bromide is eliminated to form ethene. |
| 4. Rearrangement Reaction | A reaction in which the structure of a molecule changes due to the rearrangement of atoms or groups within the molecule. | CH₃–CH₂–OH → CH₃–O–CH₂H | The atoms rearrange to form a new structure. |
🔹 Additional Types (for Advanced Study)
-
Oxidation Reactions: Addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen (e.g. alcohol → aldehyde).
-
Reduction Reactions: Addition of hydrogen or removal of oxygen (e.g. alkene → alkane).
-
Condensation Reactions: Two molecules combine with the elimination of a small molecule (like water).
🧠 Quick Summary
| Reaction Type | Main Process | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Substitution | Replacement | CH₃Cl + NaOH → CH₃OH |
| Addition | Combination | C₂H₄ + Br₂ → C₂H₄Br₂ |
| Elimination | Removal | C₂H₅OH → C₂H₄ + H₂O |
| Rearrangement | Structural shift | CH₃–CH₂–OH → CH₃–O–CH₂H |
Coming Soon