🎉 Welcome to the World of Chemistry with Inamjazbi! 🧪
Learn • Explore • Master Electrochemistry & Oxidation Numbers 🌍
📘 Model Test Questions Electrochemistry (Chapter # 12)
📝 Short-Answer Questions
Mg + H₂SO₄ → MgSO₄ + H₂
(i) Primary and secondary cell
(ii) Oxidation and reduction
(iii) Oxidizing and reducing agent
(iv) Oxidation number and valency
(i) Cr in H₂CrO₄ (ii) S in K₂S₄O₆ (iii) Fe in Fe₃O₄
(iv) Cl in HClO₄ (v) N in NH₄⁺ (vi) O in OH⁻
(vii) Al in AlF₆³⁻
(i) HNO₃ + 2HCl → NOCl + Cl₂ + 2H₂O
(ii) HgCl₂ + 2KI → HgI₂ + 2KCl
(iii) Fe₂O₃ + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO₂
(iv) PCl₃ + 3H₂O → 3HCl + H₃PO₃
(v) H₂S + Br₂ → 2HBr + S
(vi) 4NH₃ + 3O₂ → 2N₂ + 6H₂O
(vii) H₂ + Cl₂ → 2HCl
(viii) Zn + Cl₂ → ZnCl₂
(ix) 2Ca + O₂ → 2CaO
(x) 2Li + S → Li₂S
📖 Descriptive Questions
CuS + NO₃⁻ → CuSO₄ + NO (Acidic medium)
MnO₄⁻ + C₂O₄²⁻ → Mn²⁺ + CO₂ (Acidic medium)
MnO₄⁻ + Cl⁻ → Mn²⁺ + Cl₂ (Acidic medium)
MnO₄⁻ + SO₃²⁻ → Mn²⁺ + SO₄²⁻ (Acidic medium)
Cr₂O₇²⁻ + I₂ → Cr³⁺ + IO₃⁻ + H₂O (Acidic medium)
Cr₂O₇²⁻ + Fe²⁺ → Cr³⁺ + Fe³⁺ + H₂O (Acidic medium)
Cr₂O₇²⁻ + I⁻ + H⁺ → Cr³⁺ + IO₃⁻ + H₂O (Acidic medium)
NO₃⁻ + Zn → ZnO₂²⁻ + NH₃ (Basic medium)
Cr(OH)₃ + H₂O₂ → CrO₄²⁻ + OH⁻ (Basic medium)
Cl₂ + OH⁻ → Cl⁻ + ClO₃⁻ + H₂O (Basic medium)
🔋 Text Book MCQs on Electrochemistry & Oxidation Number
Pick up the best answer (Click to reveal reason)
📜 Past Papers MCQs on Electrochemistry & Oxidation Number
x+4(+1) = +1⟹ x+4=1 ⟹ x = −3 ✅ N in NH₄⁺ = −3
y+3(−2)=−1⟹y−6=−1⟹y=+5✅ N in NO₃⁻ = +5
Average = (−3+5)/2 = 2/2 =+1
(I) NH₃ + HCl → NH₄Cl
(II) 2NH₃ + 3CuO → N₂ + 3Cu + 3H₂O
(III) 2NO + O₂ → 2NO₂
(IV) 2NO₃⁻ + Cu + 4H⁺ → 2NO₂ + Cu²⁺ + 2H₂O
(I) Cl₂ → 2Cl⁻
(II) S²⁻ → S
(III) Fe²⁺ → Fe³⁺
(IV) Zn²⁺ → Zn
(I) MnO₄⁻ → Mn²⁺
(II) MnO₄²⁻ → MnO₂
(III) CrO₄²⁻ → Cr³⁺
(IV) Cr₂O₇²⁻ → 2Cr³⁺
Z has the same oxidation state (+3) in Z₂O₃ (because O = −2, 2Z + 3(−2) = 0 → 2Z − 6 = 0 → Z = +3).
Cr in CrO₃ = +6, Cr in Cr₂O₇²⁻ = +6 → same oxidation state.
2FeSO₄ + Cl₂ + H₂SO₄ → Fe₂(SO₄)₃ + 2HCl
2FeSO₄ + Cl₂ + H₂SO₄ → Fe₂(SO₄)₃ + 2HCl
Oxidation number of C = −1 (average per carbon = C–H (−4) + C–Cl (+2)). ✅
2x+2(−1)=0⟹2x−2=0⟹x=+1✅
Oxidation number of O = +1
📜 Past Papers MCQs on Electrochemistry🔋📘
Electrochemistry Chapter # 12 Test # 16
Q1. Define the terms oxidation, reduction, oxidizing agent, reducing agent and redox reactions in terms of electron transfer. Identify the oxidizing agent and reducing agent in following equation:
Mg + H₂SO₄ → MgSO₄ + H₂
🔥 Oxidation: Loss of electrons → increase in positive charge or decrease in negative charge.
Example: Fe → Fe²⁺ + 2ē
💧 Reduction: Gain of electrons → increase in negative charge or decrease in positive charge.
Example: Cu²⁺ + 2ē → Cu
🧲 Oxidizing Agent: Substance that gains electrons (causes oxidation).
Example: Br₂ accepts electrons → oxidant.
🔋 Reducing Agent: Substance that loses electrons (causes reduction).
Example: Zn loses electrons → reductant.
🔄 Redox Reaction: Simultaneous oxidation & reduction via electron transfer.
Example: Zn⁰ + 2H⁺Cl → Zn²⁺Cl₂⁻¹ + H₂⁰
Identification in given equation:
Mg → Mg²⁺ + 2ē → Oxidation 🔥 → Reducing Agent
2H⁺ + 2ē → H₂ → Reduction 💧 → Oxidizing Agent
✨ Quick Recap:
🔥 Oxidation = electron loss
💧 Reduction = electron gain
🧲 Oxidizing agent = gains electrons
🔋 Reducing agent = loses electrons
⚗️ Redox = both occur together
✅ In Mg + H₂SO₄ → MgSO₄ + H₂: Mg = Reducing Agent, H⁺ = Oxidizing Agent
Q2*. Distinguish between the following
(i) Primary and secondary cell, (ii) Oxidation and reduction
(iii) Oxidizing and reducing agent, (iv) Oxidation number and valency
Answer
🔄 Oxidation vs Reduction
1. Addition of oxygen
Example: 2Mg + O₂ → 2MgO
2. Removal of hydrogen
Example: 4NH₃ + 3O₂ → 2N₂ + 6H₂O
3. Loss of electron/De-electronation
Example: M → Mⁿ⁺ + ne⁻
M → Mn⁺ + ne⁻
5. Increase in oxidation number
7. Becoming more positive
8. Happens in reducing agents
9. Occurs at anode
1. Removal of oxygen
Example: ZnO + C → Zn + CO
2. Addition of hydrogen
Example: Cl₂ + H₂ → 2HCl
3. Gain of electron/Electronation
Example: Mⁿ⁺ + ne⁻ → M
Mn⁺ + ne⁻ → M
5. Decrease in oxidation number
7. Becoming more negative
8. Happens in oxidizing agents
9. Occurs at cathode
⚡ Oxidizing Agent vs Reducing Agent
1. gives nascent oxygen
2. accepts hydrogen
3. gains electrons
4. Oxidation number decreases
5. causes oxidation
6. Reduced itself
7. Examples: KMnO₄, K₂Cr₂O₇, H₂SO₄, HNO₃, Cl₂
1. accepts nascent oxygen
2. loses hydrogen
3. loses electrons
4. Oxidation number increases
5. causes reduction
6. Oxidized itself
7. Examples: FeSO₄, H₂C₂O₄, HCl, H₂, C, Na, Zn etc.
📊 Oxidation Number vs Valency
1. Electrons gained/lost in combined state
2. Shows extent of oxidation/reduction
3. Varies in different compounds
4. Can be +, –, 0, or fractional
5. May be zero (e.g., noble gases)
1. Number of H/Cl atoms or double O atoms combining
2. Shows combining capacity
3. Usually fixed
4. Always whole number, no sign
5. Cannot be zero (except noble gases)
🔋 Primary Cell vs Secondary Cell
1. Generates electricity by consuming chemicals
2. Cannot be recharged, disposable
3. Irreversible
4. Small voltage/capacity
5. No initial charging needed
6. Cannot be restored
Examples: Dry cell, Daniel cell, Leclanché cell, Voltaic/Galvanic cell
1. Stores electricity as chemical energy
2. Can be recharged, reusable
3. Reversible
4. Large voltage/capacity
5. Needs initial charging
6. Can be restored
Examples: Lead acid battery, Ni Cd cell, Ni Fe alkaline battery
📖 Definition
The oxidation number (oxidation state) is the apparent charge (positive, negative, or zero) on an atom in a molecule of a compound, or ion.
It can be +ve, –ve, 0, or fractional (range: –4 to +7/+8).
Example: ⚡Mn in KMnO₄ → +7 ⚡ O in H₂O₂ → –1 ⚡ Ni in Ni(CO)₄ → 0
📜 Rules for Assigning Oxidation Number
➡️Group IA → +1 (Li, Na, K etc.)
➡️Group IIA → +2 (Mg, Ca etc.)
➡️Group IIIA → +3 (Al etc.)
➡️Group IVA → ±4 (C, Si etc.)
➡️Group VA → –3/+5 (N, P etc.)
➡️Group VIA → –2/+6 (S)
➡️Group VIIA → +4 (Cl, etc.)
✨ Extra Point (Quick Tip)
Oxidation number ≠ Valency • Oxidation number can vary, be fractional, and have signs. • Valency is fixed, whole number, no sign.
⚡ Quick Recap
Free element = 0
Ion = charge
Neutral compound = sum = 0
Polyatomic ion = sum = net charge
H = +1 (normal), –1 (hydrides)
O = –2 (normal), exceptions: –1, –½, +2
F = always –1
Halogens = –1 (except with O or F)
Group rules apply systematically
Polar compounds → electronegativity decides sign
(i) Cr in H₂CrO₄ (ii) S in K₂S₄O₆
(iii) Fe in Fe₃O₄ (iv) Cl in HClO₄
H = +1, O = –2
Neutral compound → sum of oxidation numbers = 0
Equation: 2(+1) + Cr + 4(–2) = 0
⇒ +2 + Cr – 8 = 0 → Cr – 6 = 0 → Cr = +6 ✨ Chromium is in +6 oxidation state
🔹 (ii) Finding out Oxidation number of S (Sulphur) in K₂S₄O₆
K = +1, O = –2
Neutral compound → sum = 0
Equation: 2(+1) + 4S + 6(–2) = 0
⇒ +2 + 4S – 12 = 0 → 4S – 10 = 0 → 4S = +10 → Average S = +10/2 → ✨Average S = +2.5
📌 Alternate Method (from structure):
Two terminal S atoms = +5 each
Two central S atoms (S*) = 0 each (pure covalent bond)
Total of 4 S atoms = 5+0+0+5=10
Average S = 10/4 = +2.5 ✨ Sulphur shows mixed oxidation states (0 and +5), average = +2.5
🔹 (iii) Finding out Oxidation number of Fe (Iron) in Fe₃O₄
Equation: 3Fe + 4(–2) = 0 → 3Fe – 8 = 0 → 3Fe = +8 → Fe = +8/3 ✨ Iron has mixed oxidation states (+2 and +3), average = +2.66
📌 Alternate Method:
Mixed oxide: FeO (Fe = +2) + Fe₂O₃ (Fe = +3)
Average oxidation state = (1×+2 + 2×+3)/3 = +8/3 ≈ +2.66
🔹 (iv) Finding out Oxidation number of Cl (Chlorine) in HClO₄
H = +1, O = –2
Equation: (+1) + Cl + 4(–2) = 0
⇒ +1 + Cl – 8 = 0 → Cl – 7 = 0 → Cl = +7 ✨ Chlorine is in +7 oxidation state
🔹 (v) Finding out Oxidation number of Nitrogen in NH₄⁺
H = +1
Total charge = +1
Equation: N + 4(+1) = +1
N + 4 = +1 → N = –3 ✨ Nitrogen = –3 oxidation state
🔹 (vi) Finding out Oxidation number of Oxygen in OH⁻
H = +1
Total charge = –1
Equation: O + (+1) = –1
O + 1 = –1 → O = –2 ✨ Oxygen = –2 oxidation state
🔹 (vii) Finding out Oxidation number of Aluminium in AlF₆³⁻
F = –1 (always)
Total charge = –3
Equation: Al + 6(–1) = –3
Al – 6 = –3 → Al = +3 ✨ Aluminium = +3 oxidation state
⚡ Quick Recap
Cr in H₂CrO₄ → +6 🔥
S in K₂S₄O₆ → Mixed (0, +5), average +2.5 🌀
Fe in Fe₃O₄ → Mixed (+2, +3), average +2.66 ⚙️
Cl in HClO₄ → +7 🌟
N in NH₄⁺ → –3 🌀
O in OH⁻ → –2 💧
Al in AlF₆³⁻ → +3 🔥
(i) 2HCl + HNO₃ → NOCl + Cl₂ + 2H₂O
(ii) HgCl₂ + 2KI → HgI₂ + 2KCl
(iii) Fe₂O₃ + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO₂
(iv) PCl₃ + 3H₂O → 3HCl + H₃PO₃
(v) 4NH₃ + 3O₂ → 2N₂ + 6H₂O
(vi) H₂ + Cl₂ → 2HCl
(vii) Zn + Cl₂ → ZnCl₂
(viii) H₂S + Br₂ → 2HBr + S
(ix) 2Ca + O₂ → CaO
(x) 2Li + S → Li₂S
✨ (i) 2HCl (RA) + HNO₃ (OA) → NOCl + Cl₂ + 2H₂O ➡️ Redox ✅ — HCl oxidized, HNO₃ reduced.
✨ (ii) HgCl₂ + 2KI → HgI₂ + 2KCl ➡️ Non redox ❌ — Ion exchange only.
✨ (iii) Fe₂O₃ (OA) + 3CO (RA) → 2Fe + 3CO₂ ➡️ Redox ✅ — CO oxidized, Fe₂O₃ reduced.
✨ (iv) PCl₃ + 3H₂O → 3HCl + H₃PO₃ ➡️ Non redox ❌ — Hydrolysis/substitution.
✨ (v) 4NH₃ (RA) + 3O₂ (OA) → 2N₂ + 6H₂O ➡️ Redox ✅ — NH₃ oxidized, O₂ reduced.
✨ (vi) H₂ (RA) + Cl₂ (OA) → 2HCl ➡️ Redox ✅ — H₂ oxidized, Cl₂ reduced.
✨ (vii) Zn (RA) + Cl₂ (OA) → ZnCl₂ ➡️ Redox ✅ — Zn oxidized, Cl₂ reduced.
✨ (viii) H₂S (RA) + Br₂ (OA) → 2HBr + S ➡️ Redox ✅ — H₂S oxidized, Br₂ reduced.
✨ (ix) 2Ca (RA) + O₂ (OA) → CaO ➡️ Redox ✅ — Ca oxidized, O₂ reduced.
✨ (x) 2Li (RA) + S (OA) → Li₂S ➡️ Redox ✅ — Li oxidized, S reduced.
✨ Quick cues:
RA (reducing agent) → gets oxidized 🔥
OA (oxidizing agent) → gets reduced 💧
Non redox = no change in oxidation numbers ↔️
❷ Na → RA 🔋 Reason: Sodium being metal is highly electropositive → donates electrons → reducing agent.
❸ H₂S → RA 🔋 Reason: Sulphur in H₂S (binary acid) can be oxidized to elemental S → reducing agent.
❹ H₂SO₄ → OA 🧲 Reason: Concentrated sulphuric acid being oxyacid accepts electrons (strong oxidizer).
❺ KMnO₄ → OA 🧲 Reason: Mn⁷⁺ in KMnO₄ being oxysalt gets reduced → powerful oxidizing agent.
❻ Zn → RA 🔋 Reason: Zinc being metal loses electrons to form Zn²⁺ → reducing agent.
✨ Quick Recap:
🔋 Reducing agents: Al, Na, H₂S, Zn (they lose electrons).
🧲 Oxidizing agents: H₂SO₄, KMnO₄ (they gain electrons).
❶ H₂SO₃ 👉 2(+1) + S + 3(–2) = 0 👉 +2 + S – 6 = 0 → S = +4 ✨ Sulphur = +4
❷ S₂O₃²⁻ (Thiosulphate ion) 👉 2S + 3(–2) = –2 👉 2S – 6 = –2 → 2S = +4 → S = +2 (average)
✨ Sulphur shows mixed states (one S often +5, one S often –1), average = +2
❸ S₂Cl₂ (Disulphur dichloride) 👉 2S + 2(–1) = 0 👉 2S – 2 = 0 → 2S = +2 → S = +1 ✨ Sulphur = +1
❹ SF₆ (Sulphur hexafluoride) 👉 S + 6(–1) = 0 👉 S – 6 = 0 → S = +6 ✨ Sulphur = +6
❺ SO₂Cl₂ (Sulphuryl chloride) 👉 S + 2(–2) + 2(–1) = 0 👉 S – 6 = 0 → S = +6 ✨ Sulphur = +6
⚡ Quick Recap
🧪 H₂SO₃ → S = +4
🔋 S₂O₃²⁻ → S (average) = +2 (mixed states possible)
🌿 S₂Cl₂ → S = +1
🌟 SF₆ → S = +6
💥 SO₂Cl₂ → S = +6
✨ Note: Sulphur is versatile — it can show oxidation states from –2 up to +6 depending on the compound.
❶ CrO₃ 👉 Cr + 3(–2) = 0 👉 Cr – 6 = 0 → Cr = +6 ✨ Chromium = +6 oxidation state
❷ CrO₂ 👉 Cr + 2(–2) = 0 👉 Cr – 4 = 0 → Cr = +4 ✨ Chromium = +4 oxidation state
❸ Cr₂O₇²⁻ (Dichromate ion) 👉 2Cr + 7(–2) = –2 👉 2Cr – 14 = –2 → 2Cr = +12 → Cr = +6 ✨ Chromium = +6 OS
❹ CrO₂⁻ 👉 Cr + 2(–2) = –1 👉 Cr – 4 = –1 → Cr = +3 ✨ Chromium = +3 oxidation state
❺ CrO₂Cl₂ (Chromyl chloride) 👉 Cr + 2(–2) + 2(–1) = 0 👉 Cr – 6 = 0 → Cr = +6 ✨ Chromium = +6 OS
⚡ Quick Recap
CrO₃ → Cr = +6 🔥
CrO₂ → Cr = +4 ⚙️
Cr₂O₇²⁻ → Cr = +6 🌟
CrO₂⁻ → Cr = +3 💧
CrO₂Cl₂ → Cr = +6 🧪
✨ Chromium shows variable oxidation states (+3, +4, +6), highlighting its versatility in redox chemistry.
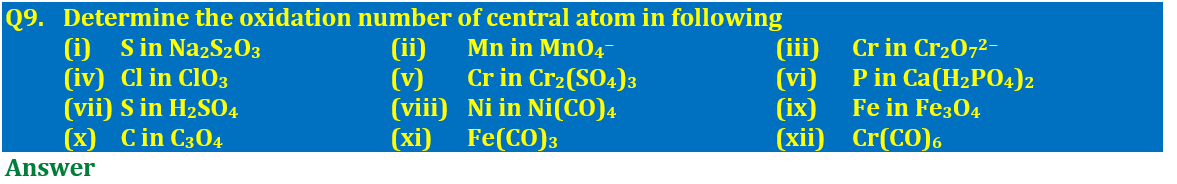
(i) S in Na₂S₂O₃ (ii) Mn in MnO₄⁻ (iii) Cr in Cr₂O₇²⁻
(iv) Cl in ClO₃ (v) Cr in Cr₂(SO₄)₃ (vi) P in Ca(H₂PO₄)₂
(vii) S in H₂SO₄ (viii) Ni in Ni(CO)₄ (ix) Fe in Fe₃O₄
(x) C in C₃O₄ (xi) Fe in Fe(CO)₃ (xii) Cr in Cr(CO)₆
Na = +1, O = –2
Neutral compound → sum of oxidation numbers = 0
Equation: 2(+1) + 2S + 3(–2) = 0 👉 +2 + 2S – 6 = 0 → 2S – 4 = 0 → 2S = +4 → S = +4/2 → S = +2 (average)
✨ One S = –2, other S = +6 → average = +2 🌀
Alternate Method
In Na₂S₂O₃, one S-atom (S*) has oxidation number = −2 while the other S-atom (S**) has oxidation number = +6. The total oxidation number of both S atoms = −2 + (+6) = +4
The average oxidation number of S = Total Oxidation number/2 = +4/2 = +2
🔹 (ii) Finding out Oxidation number of Mn in MnO₄⁻
O = –2
Equation: Mn + 4(–2) = –1 👉 Mn – 8 = –1 → Mn = +7 ✨ Mn = +7 ⚡ (strong oxidizer)
🔹 (iii) Finding out Oxidation number of Cr in Cr₂O₇²⁻
O = –2
Polyatomic ions = sum = net charge
Equation: 2Cr + 7(–2) = –2 👉 2Cr – 14 = –2 → 2Cr = +12 → Cr = +6 ✨ Cr = +6 🔥
🔹 (iv) Finding out Oxidation number of Cl in ClO₃
O = –2
Equation: Cl + 3(–2) = 0 👉 Cl – 6 = 0 → Cl = +6 ✨ Cl = +6 🌟
🔹 (v) Finding out Oxidation number of Cr in Cr₂(SO₄)₃
SO₄ = –2
Equation: 2Cr + 3(–2) = 0 👉 2Cr – 6 = 0 → 2Cr = +6 → Cr = +3 ✨ Cr = +3 ⚙️
🔹 (vi) Finding out Oxidation number of P in Ca(H₂PO₄)₂
Ca = +2, H = +1, O = –2
Equation: (+2) + 4(+1) + 2P + 8(–2) = 0 👉 +2 + 4 + 2P – 16 = 0 → 2P – 10 = 0 → 2P = +10 → P = +5 ✨ P = +5 🧪
🔹 (vii) Finding out Oxidation number of S in H₂SO₄
H = +1, O = –2
Equation: 2(+1) + S + 4(–2) = 0 👉 +2 + S – 8 = 0 → S – 6 = 0 → S = +6 ✨ S = +6 💥
🔹 (viii) Finding out Oxidation number of Ni in Ni(CO)₄
CO = neutral ligand (0)
Equation: Ni + 4(0) = 0 → Ni = 0 ✨ Ni = 0 ⚡ (metal carbonyl complex)
🔹 (ix) Finding out Oxidation number of Fe in Fe₃O₄
O = –2
Equation: 3Fe + 4(–2) = 0 👉 3Fe – 8 = 0 → 3Fe = +8 → Fe = +8/3 ≈ +2.66
✨ Mixed valency: Fe²⁺ & Fe³⁺ 🌀
🔹 (x) Finding out Oxidation number of C in C₃O₄
O = –2
Equation: 3C + 4(–2) = 0 👉 3C – 8 = 0 → 3C = +8 → C = +8/3 ≈ +2.66 ✨ C = +2.66 🌿
🔹 (xi) Finding out Oxidation number of Fe in Fe(CO)₃
CO = neutral ligand (0)
Equation: Fe + 3(0) = 0 → Fe = 0 ✨ Fe = 0 ⚡
🔹 (xii) Finding out Oxidation number of Cr in Cr(CO)₆
CO = neutral ligand (0)
Equation: Cr + 6(0) = 0 → Cr = 0 ✨ Cr = 0 🧲
⚡ Quick Recap
Na₂S₂O₃ → S (Average) = +2 (✨ Sulphur shows mixed states 🌀, one S = –2, one S = +6)
MnO₄⁻ → Mn = +7 (✨ Maximum oxidation state; Strong oxidizer ⚡)
Cr₂O₇²⁻ → Cr = +6 (✨ Chromium in highest state 🔥; Strong oxidizer)
ClO₃ → Cl = +6 (✨ Chlorine highly oxidized 🌟)
Cr₂(SO₄)₃ → Cr = +3 (✨ Chromium in moderate state ⚙️)
Ca(H₂PO₄)₂ → P = +5 (Phosphorus pentavalent)
H₂SO₄ → S = +6 💥
Ni(CO)₄ → Ni = 0 ⚡
Fe₃O₄ → Average Fe = +8/3 ≈ +2.66 (Fe²⁺ & Fe³⁺, Mixed valency 🌀)
C₃O₄ → Average C = +8/3 ≈ +2.66 (✨ Carbon in mixed state 🌿)
Fe(CO)₃ → Fe = 0 ✨ Neutral ligand complex ⚡
Cr(CO)₆ → Cr = 0 ✨ Neutral ligand complex 🧲
(i) C in C₂H₆O (ii) C in C₄H₈O₂ (iii) C in CH₃Cl (iv) Cr in CrO₂Cl₂
(v) C in COCl₂ (vi) N in NOCl (vii) UO₂Cl₂ (viii) BiOCl
(ix) S in SO₂Cl₂ (x) S in SOCl₂ (xi) S in HSO₃F (xii) C in HCNS
(xiii) P in POCl₃ (xiv) CNO⁻ (xv) Cl in CaOCl₂ (Bleaching powder)
(xvi) S in Na₂S₄O₆ (xvii) N in NH₄NO₃ (xviii) Br in BrO₃⁻
Note
In few organic compounds and in few inorganic compounds where two more electronegative elements are present, more than one element has negative oxidation number while only one element has positive oxidation number.
🔹 (i) C in C₂H₆O
H = +1, O = –2
Equation: 2C + 6(+1) + (–2) = 0 👉 2C + 6 – 2 = 0 → 2C + 4 = 0 → 2C = –4 → C = –2 ✨ Carbon = –2 🌀
🔹 (ii) C in C₄H₈O₂
H = +1, O = –2
Equation: 4C + 8(+1) + 2(–2) = 0 👉 4C + 8 – 4 = 0 → 4C + 4 = 0 → 4C = –4 → C = –1 ✨ Carbon = –1 ⚡
🔹 (iii) C in CH₃Cl
H = +1, Cl = –1
Equation: C + 3(+1) + (–1) = 0 👉 C + 3 – 1 = 0 → C + 2 = 0 → C = –2 ✨ Carbon = –2 🌿
🔹 (iv) Cr in CrO₂Cl₂
O = –2, Cl = –1
Equation: Cr + 2(–2) + 2(–1) = 0 👉 Cr – 4 – 2 = 0 → Cr – 6 = 0 → Cr = +6 ✨ Chromium = +6 🔥
🔹 (v) C in COCl₂ (Phosgene)
O = –2, Cl = –1
Equation: C + (–2) + 2(–1) = 0 👉 C – 4 = 0 → C = +4 ✨ Carbon = +4 🌟
🔹 (vi) N in NOCl
O = –2, Cl = –1
Equation: N + (–2) + (–1) = 0 👉 N – 3 = 0 → N = +3 ✨ Nitrogen = +3 🧪
🔹 (vii) U in UO₂Cl₂
O = –2, Cl = –1
Equation: U + 2(–2) + 2(–1) = 0 👉 U – 6 = 0 → U = +6 ✨ Uranium = +6 ⚡
🔹 (viii) Bi in BiOCl
O = –2, Cl = –1
Equation: Bi + (–2) + (–1) = 0 👉 Bi – 3 = 0 → Bi = +3 ✨ Bismuth = +3 🌿
🔹 (ix) S in SO₂Cl₂
O = –2, Cl = –1
Equation: S + 2(–2) + 2(–1) = 0 👉 S – 6 = 0 → S = +6 ✨ Sulphur = +6 💥
🔹 (x) S in SOCl₂
O = –2, Cl = –1
Equation: S + (–2) + 2(–1) = 0 👉 S – 4 = 0 → S = +4 ✨ Sulphur = +4 🧲
🔹 (xi) S in HSO₃F
H = +1, O = –2, F = –1
Equation: (+1) + S + 3(–2) + (–1) = 0 👉 1 + S – 6 – 1 = 0 → S – 6 = 0 → S = +6 ✨ Sulphur = +6 ⚡
🔹 (xii) C in HCNS
H = +1, N = –3, S = –2
Equation: (+1) + C + (–3) + (–2) = 0 👉 C – 4 = 0 → C = +4 ✨ Carbon = +4 🌟
🔹 (xiii) P in POCl₃
O = –2, Cl = –1 (since Cl is more electronegative than P)
Equation: P + (–2) + 3(–1) = 0 👉 P – 5 = 0 → P = +5 ✨ Phosphorus = +5 🧪
🔹 (xiv) C in CNO⁻
O = –2, N = –3 (since N is more electronegative than C)
Equation: C + (–3) + (–2) = –1 👉 C – 5 = –1 → C = –1 +5 → C = +4 ✨ Carbon = +4 🌿
🔹 (xv) Cl in CaOCl₂ (Bleaching powder)
👉 Mixed salt (containing two anions):
One Cl = –1 (chloride ion)
One Cl = +1 (hypochlorite ion)
✨ Chlorine shows two states: –1 & +1. Average oxidation state of Cl = 0 🌀
🔹 (xvi) S in Na₂S₄O₆
Na = +1, O = –2
👉 End S atoms = +5 each, middle S atoms = 0 each 👉 Total = 5+0+0+5 =10 → Average = 10/4 = +2.5 ✨ Sulphur = +2.5 (average) 🧲
🔹 (xvii) N in NH₄NO₃ (ammonium nitrate)
👉 Two types of N in two types of ionic species:
In NH₄⁺ → N + 4(+1) = +1 👉 N + 4 = +1 → N = +1 – 4 → N = –3 ✨ Nitrogen = –3
In NO₃⁻ → 🔹 (xviii) Br in BrO₃⁻
O = –2
Equation: Br + 3(–2) = –1 👉 Br – 6 = –1 → Br = +5 ✨ Bromine = +5 💥
⚡ Quick Recap
C in C₂H₆O → –2
C in C₄H₈O₂ → –1
C in CH₃Cl → –2
Cr in CrO₂Cl₂ → +6
C in COCl₂ → +4
N in NOCl → +3
U in UO₂Cl₂ → +6
Bi in BiOCl → +3
S in SO₂Cl₂ → +6
S in SOCl₂ → +4
S in HSO₃F → +6
C in HCNS → +4
P in POCl₃ → +5
C in CNO⁻ → +4
Cl in CaOCl₂ → –1 & +1 (average 0)
S in Na₂S₄O₆ → +2.5 (average)
N in NH₄NO₃ → –3, +5 (average +1)
Br in BrO₃⁻ → +5
👉 Reason in one line: Cathode attracts positive metal ions → they gain electrons → form coating on the surface. 🌟
👉 What is corrosion? Corrosion is the gradual destruction of metals when they react with moisture, oxygen, or other chemicals in the environment. 🌧️⚙️
👉 Causes of corrosion:
• Presence of water/moisture 💧
• Oxygen in air 🌬️
• Acids, salts, pollutants in surroundings 🧪
👉 Prevention methods:
• Painting / Oiling / Greasing 🎨🛢️ (forms protective layer)
• Galvanization / Electroplating ⚡ (coating with another metal)
• Alloying 🔩 (using corrosion resistant alloys like stainless steel)
• Cathodic protection 🔋 (sacrificial anode method)
👉 Properties of Electrochemical Series:
1. Order of Reactivity 🔥
o Metals with more negative E° values are strong reducing agents (e.g., K, Na, Ca).
o Non metals with more positive E° values are strong oxidizing agents (e.g., F₂, Cl₂).
2. Prediction of Displacement Reactions 🔄
o A metal higher in the series can displace a metal lower from its salt solution.
3. Electropositivity Trend 📉
o Electropositivity of metals decreases down the series (K > Na > Ca > Zn > Cu).
4. Oxidizing & Reducing Strength 🧲
o Elements at the top (like F₂) are strong oxidizers.
o Elements at the bottom (like Li, K) are strong reducers.
5. Electrochemical Cell EMF ⚡
o The difference in electrode potentials of two metals gives the EMF of the cell.
6. Corrosion Prediction 🌧️
o Metals lower in the series (like Fe) corrode more easily than noble metals (like Au, Pt).
7. Electroplating & Extraction 🎨
o Helps in selecting suitable metals for electroplating and extraction processes.
✨ In short: Electrochemical series = list of elements by E° values → predicts reactivity, displacement, corrosion, and cell EMF.
👉 Electrochemistry: Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry that studies the relationship between electricity and chemical reactions, especially redox processes. 🧪
⚡ Redox Parts in Electrolysis of Molten CaCl₂ / NaCl
1. Oxidation (Loss of electrons) 🔥
o Occurs at the anode (+).
o Example: Cl⁻ → Cl₂ + 2e⁻
o Chloride ions are oxidized to chlorine gas. 🌬️
2. Reduction (Gain of electrons) 💧
o Occurs at the cathode (–).
o Example: Ca²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Ca (metal)
o Calcium (or sodium) ions are reduced to metal and deposited. ✨
🔹 Electrolysis of Molten CaCl₂ (same for NaCl)
• At Cathode (–): Ca²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Ca (metal deposited) 🪙
• At Anode (+): 2Cl⁻ → Cl₂ (gas liberated) 🌬️
Overall Reaction: CaCl₂ → Ca (metal) + Cl₂ (gas)
✨ In short: Electrolysis = redox in action → Reduction at cathode (metal deposition) & Oxidation at anode (gas release).
Tendency of an electrode to undergo redox (lose/gain electrons).
It is the difference of potential created between a metal electrode and 1 molar solution of its ion (salt).
🔋 Standard Electrode Potential (E°):
It is the difference of potential created between a metal electrode and 1 molar (1M) solution of its ion (salt) measured at 25°C, 1 atm.
🌟 Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE)
➡️ Reference electrode with E° = 0.00 V.
➡️ Consists of Pt rod in 1M H⁺ solution, H₂ gas bubbled at 1 atm and 25°C.
➡️ Equilibrium: H₂ ⇌ 2H⁺ + 2ē E° = 0.00 V
➡️ Acts as anode (oxidation) or cathode (reduction) depending on cell.
H₂ (g) → 2H⁺ (aq) + 2ē ………….... Oxidation E° = 0.0 V (SHE acts as anode)
2H⁺ (aq) + 2ē → H₂ (g) ……………. Reduction E° = 0.0 V (SHE acts as cathode)
🔧 Construction and Working (Cell Reactions) of Zinc-SHE Galvanic Cell
🟦 Anode Half-Cell: Zn in 1M ZnSO₄ → Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2ē (oxidation); E° = ?
🟥 Cathode Half-Cell: SHE (inert Pt electrode in 1 M HCl, H₂ gas at 1 atm) → 2H⁺ + 2ē → H₂ (reduction); E°= 0.0V.
🌉 Salt Bridge: Inert KCl salt bridge: balances charge, prevents mixing; anions → anode, cations → cathode.
📊 Voltmeter; Both electrodes are connected with voltmeter giving positive cell potential (E°).
🔋 Cell Potential: +0.76 V (electrons flow Zn → SHE). Zn + 2H⁺ → Zn²⁺ + H₂ E°cell = +0.76V
➡️ E°cell = E°cathode − E°anode
➡️ E°cell = E°reduction − E°oxidation
➡️ E°cell = E°H₂ − E°Zn
➡️ 0.76 = 0.000 − E°Zn
➡️ E°Zn = −0.76 V (reduction potential by conventions) (✨ negative sign signifies that actually the reaction at zinc electrode occurs in opposite direction i.e. it is the oxidation rather than reduction which occurs at zinc)
➡️ E°(oxidation of Zn) = +0.76 V
🏁 Result
➡️ E°(oxidation of Zn) = +0.76 V
➡️ E°(reduction of Zn) = –0.76 V ✨ Zinc electrode is negative vs SHE.
📐 Cell Diagram
Zn–SHE: Zn | Zn²⁺ || H⁺ | H₂ | (Pt) (flow of electrons takes place from zinc to SHE.)
➡️ Electrode potential = measure of redox tendency.
➡️ SHE = universal reference (0.00 V).
➡️ Zn–SHE cell: Zn oxidized, H⁺ reduced → E° = –0.76 V for Zn.
➡️ Cu–SHE cell: H₂ oxidized, Cu²⁺ reduced → E° = +0.34 V for Cu.
➡️ Salt bridge ensures ion flow and charge balance.
🔹 Experimental Measurement of Electrode Potential of Copper in SHE-Copper Cell
🔧 Construction and Working (Cell Reactions) of SHE-Copper Cell
🟦 Anode Half-Cell: SHE (inert Pt electrode in 1 M HCl, H₂ gas at 1 atm) → H₂ → 2H⁺ + 2ē (oxidation); E° = 0.0V
🟥 Cathode Half-Cell: Zn in 1M ZnSO₄ → Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu (reduction); E°= ?
🌉 Salt Bridge: Inert KCl salt bridge: balances charge, prevents mixing; anions → anode, cations → cathode.
📊 Voltmeter; Both electrodes are connected with voltmeter giving positive cell potential (E°).
🔋 Cell Potential: +0.34 V (electrons flow SHE → Cu). H₂ + Cu²⁺ → Cu + H₂ E°cell = +0.34 V
➡️ E°cell = E°cathode − E°anode
➡️ E°cell = E°reduction − E°oxidation
➡️ E°cell = E°Cu − E°H₂
➡️ 0.34 = E°Cu − 0.000
➡️ E°Cu = +0.34 V (reduction potential by conventions)
➡️ E°(oxidation of Cu) = −0.34 V
🏁 Result
E°(reduction of Cu) = +0.34 V
E°(oxidation of Cu) = –0.34 V ✨ Copper electrode is positive vs SHE.
📐 Cell Diagrams of SHE–Cu Cell
(Pt) | H₂ | H⁺ || Cu²⁺ | Cu (flow of electrons takes place from SHE to copper.)
Definition: It is a type of electrochemical cell where spontaneous redox reaction generates electricity 🔋.
✨ In short: A Galvanic cell = two half cells + salt bridge → spontaneous redox → electricity generated.
🔧 Construction:
🧪 Made of two half cells → each has a metal strip dipped in its own ion solution.
🔌 Connections: 📟 Half cells connected via voltmeter (to measure EMF) and salt bridge (to balance charge).
🔩 Electrodes:
➕ Cathode = positive (reduction occurs).
➖ Anode = negative (oxidation occurs).
🌉 Salt Bridge: U shaped tube with inert electrolyte gel. Balance charge, prevents mixing; anions → anode, cations → cathode.
🔥 Anode (oxidation at zinc half-cell): Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2ē
✨ Cathode (reduction at copper half-cell): Cu²⁺ + 2ē → Cu
⚡ Overall Cell Reaction (add both reactions): Zn + Cu²⁺ → Zn²⁺ + Cu; E°cell = 1.11 V
🧾 Cell Diagram (Cell notation):
⚡ Cell notation is a shorthand symbolic notation used to represent an electrochemical cell, showing the anode, cathode, electrolytes, and salt bridge in a specific order.
Zn | Zn²⁺ (1M) || Cu²⁺ (1M) | Cu
⚡ ➖➖ Double vertical line ( || ) represents the salt bridge 🌉
⚡ Electron Flow: ➖ From Zn anode → ➕ To Cu cathode (Zn → Cu)
✨ In short: Copper–zinc Galvanic cell = Zn oxidizes, Cu²⁺ reduces, electrons flow Zn → Cu, producing 1.11 V.
| ⚡ Primary Cell | 🔄 Secondary Cell |
|---|---|
| Generates electricity by consuming chemicals | Stores electricity as chemical energy |
| Cannot be recharged, disposable (Single use) | Can be recharged, reusable (Multiple use) |
| Irreversible reaction | Reversible reaction |
| Small voltage/capacity | Large voltage/capacity |
| No initial charging needed | Needs initial charging |
| Cannot be restored | Can be restored |
| Examples: Dry cell, Daniel cell, Leclanché cell, Voltaic/Galvanic cell | Examples: Lead acid battery, Ni Cd cell, Ni Fe alkaline battery |
| Cheaper | More expensive |
| Short life | Long life |
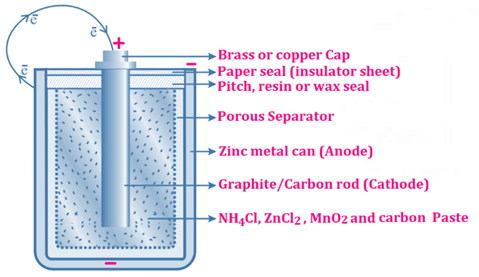
🔩 Zinc (Anode): gets oxidized to Zn²⁺ (enters the moist paste) releasing electrons.
⚡ Electrons flow: Zn anode → Graphite cathode through wire
🪙 Graphite (Cathode): Mn⁴⁺ reduced to Mn³⁺ ions.
🔋 Cell voltage: 1.5 V
❌ Cell becomes dead after complete use of zinc
🔥 Anode Reaction (Oxidation): Zn(s) → Zn²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⚡
❄️ Cathode Reaction (Reduction): 2NH₄⁺ + 2MnO₂ + 2e⁻ → Mn₂O₃ + 2NH₃ + H₂O 🧪
CuS + NO₃⁻ → CuSO₄ + NO (Acidic medium)
MnO₄⁻ + C₂O₄²⁻ → Mn²⁺ + CO₂ (Acidic medium)
MnO₄⁻ + Cl⁻ → Mn²⁺ + Cl₂ (Acidic medium)
MnO₄⁻ + SO₃²⁻ → Mn²⁺ + SO₄²⁻ (Acidic medium)
Cr₂O₇²⁻ + I₂ → Cr³⁺ + IO₃⁻ + H₂O (Acidic medium)
Cr₂O₇²⁻ + Fe²⁺ → Cr³⁺ + Fe³⁺ + H₂O (Acidic medium)
Cr₂O₇²⁻ + I⁻ + H⁺ → Cr³⁺ + IO₃⁻ + H₂O (Acidic medium)
NO₃⁻ + Zn → ZnO₂²⁻ + NH₃ (Basic medium)
Cr(OH)₃ + H₂O₂ → CrO₄²⁻ + OH⁻ (Basic medium)
Cl₂ + OH⁻ → Cl⁻ + ClO₃⁻ + H₂O (Basic medium)
Solution
👉 N⁺⁵O₃⁻ (OA) + H₂S⁻² (RA) → N⁺²O + S⁰
Reduction (N): NO₃⁻ → NO (3ē gain)
H₂S → S + 2H⁺ + 2ē (Charge zero LHS = charge zero RHS)
NO₃⁻ + 4H⁺ + 3ē → NO + 2H₂O (Charge zero LHS = charge zero RHS)
Reduction × 2 → 6ē
Simplify H⁺: 2HNO₃ + 3H₂S → 3S + 2NO + 2H₂O (Charge zero LHS = charge zero RHS)
✨ Final Balanced Equation (acidic medium): 3H₂S + 2HNO₃ → 3S + 2NO + 2H₂O 🌟
✂️ Split → Oxidation & Reduction
🔄 Balance e⁻ (×3, ×2)
➕ Add → Cancel → Simplify
✅ Final Balanced Equation
👉 S²⁻ (RA) + N⁺⁵O₃⁻ (OA) → S⁺⁶O₄²⁻ + N⁺²O ✅
💧 Reduction (N): NO₃⁻ → NO (3ē gain) ✅🟢
S²⁻ + 4H₂O → SO₄²⁻ + 8H⁺ + 8ē (–2 charge LHS = –2 charge RHS) ✅
NO₃⁻ + 4H⁺ + 3ē → NO + 2H₂O (Charge zero LHS = charge zero RHS) ✅
💧 Reduction (3ē) × 8 → 24ē
Simplify H⁺/H₂O: 8NO₃⁻ + 8H⁺ + 3S²⁻ → 3SO₄²⁻ + 8NO + 4H₂O (–6 charge LHS = –6 charge RHS) ✅
✨ Final Balanced Equation (acidic medium): 3CuS + 8HNO₃ → 3CuSO₄ + 8NO + 4H₂O ✅🌟
[Equation is already ionic, only write oxidation number of central atoms]
🔥 Oxidation (C): C in C₂O₄²⁻ goes from +3 → +4 in CO₂ (2C atoms → total 2e⁻ loss per atom, 2×2=4ē) 🟠
💧 Reduction (Mn): Mn in MnO₄⁻ goes from +7 → +2 in Mn²⁺ (5ē gain per Mn) 🟢
💧 Reduction (Mn): MnO₄⁻ → Mn²⁺ (3ē gain) ✅🟢
Equation: C₂O₄²⁻ → 2CO₂ + 2ē (–2 charge LHS = –2 charge RHS) ✅
Equation: MnO₄⁻ + 8H⁺ + 5ē → Mn²⁺ + 4H₂O (+2 charge LHS = +2 charge RHS) ✅
💧 Reduction (5ē) × 2 = 10ē ➡️ 2MnO₄⁻ + 16H⁺ + 10ē → 2Mn²⁺ + 8H₂O
✨ Final Balanced Equation (acidic medium): 2MnO₄⁻ + 5C₂O₄²⁻ + 16H⁺ → 2Mn²⁺ + 10CO₂ + 8H₂O ✅🌟
[Equation is already ionic, only write oxidation number of central atoms and cancel spectator ion H⁺ with H₂O]
🔥 Oxidation (I): I in I⁻ goes from –1 → +5 in IO₃⁻ (6ē lost) 🟠
💧 Reduction (Cr): Cr in Cr₂O₇²⁻ goes from +6 → +3 in Cr³⁺ (2 Cr atoms → total 3ē gain per atom, 3×2 = 6ē gained) 🟢
💧 Reduction (Cr): Cr₂O₇²⁻ → 2Cr³⁺ (3ē per Cr → total 6ē gain) ✅🟢
Equation: I⁻ + 3H₂O → IO₃⁻ + 6H⁺ + 6ē (–1 charge LHS = –1 charge RHS) ✅
Equation: Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 14H⁺ + 6ē → 2Cr³⁺ + 7H₂O (+6 charge LHS = +6 charge RHS) ✅
💧 Reduction: 6ē ➡️ Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 14H⁺ + 6ē → 2Cr³⁺ + 7H₂O
(Same electrons, no need for further balancing)
Simplify H⁺/H₂O: I⁻ + Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 8H⁺ → IO₃⁻ + 2Cr³⁺ + 4H₂O (+5 charge LHS = +5 charge RHS) ✅
✨ Final Balanced Equation (acidic medium): I⁻ + Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 8H⁺ → IO₃⁻ + 2Cr³⁺ + 4H₂O ✅🌟
[Equation is already ionic, only write oxidation number of central atoms]
🔥 Oxidation (Cr): Cr in Cr(OH)₃ goes from +3 → +6 in CrO₄²⁻ (3ē lost) 🟠
💧 Reduction (S): S in SO₄²⁻ goes from +6 → +4 in SO₃²⁻ (2ē gained) 🟢
💧 Reduction (S): SO₄²⁻ → SO₃²⁻ (2ē gain) ✅🟢
Equation: Cr(OH)₃ + H₂O → CrO₄²⁻ + 5H⁺ + 3ē (0 charge LHS = 0 charge RHS) ✅
⚡ Convert to basic medium: add OH⁻ to neutralize H⁺ forming H₂O, then simplify 💧
Equation: Cr(OH)₃ + 5OH⁻ → CrO₄²⁻ + 4H₂O + 3ē (–5 charge LHS = –5 charge RHS) ✅
Equation: SO₄²⁻ + 2H⁺ + 2ē → SO₃²⁻ + H₂O (–2 charge LHS = –2 charge RHS) ✅
⚡ Convert to basic medium: add OH⁻ to neutralize H⁺ forming H₂O, then simplify 💧
Equation: SO₄²⁻ + H₂O + 2ē → SO₃²⁻ + 2OH⁻ (–4 charge LHS = –4 charge RHS) ✅
💧 Reduction 2ē × 3 = 6ē ➡️ 3SO₄²⁻ + 3H₂O + 6ē → 3SO₃²⁻ + 6OH⁻
Simplify OH⁻: 2Cr(OH)₃ + 3SO₄²⁻ + 4OH⁻ → 2CrO₄²⁻ + 3SO₃²⁻ + 5H₂O (–10 charge LHS = –10 charge RHS) ✅
✨ Final Balanced Equation (basic medium): 2Cr(OH)₃ + 3SO₄²⁻ + 4OH⁻ → 2CrO₄²⁻ + 3SO₃²⁻ + 5H₂O ✅🌟
[Equation is already ionic, only write oxidation number of central atoms]
This is an auto-redox (disproportionation) reaction, because chlorine is both oxidized and reduced. So, both OH⁻ and H₂O are omitted from it.
Cl₂ → Cl⁻ + ClO₃⁻
💧 Oxidation (Cl): Cl in Cl₂ goes from 0 → +5 in ClO₃⁻ (10ē lost per total 2Cl) 🟢
🔥 Reduction (Cl): Cl in Cl₂ goes from 0 → –1 in Cl⁻ (2ē gained per total 2Cl) 🟠
💧 Reduction (Cl): Cl₂ → 2Cl⁻ (2Cl atoms → 1ē gain per atom, 1×2 = 2ē gained total) ✅🟢
Equation: Cl₂ + 6H₂O → 2ClO₃⁻ + 12H⁺ + 10ē (0 charge LHS = 0 charge RHS) ✅
⚡ Convert to basic medium: add OH⁻ to neutralize H⁺ forming H₂O, then simplify 💧
Equation: Cl₂ + 12OH⁻ → 2ClO₃⁻ + 6H₂O + 10ē (–12 charge LHS = –12 charge RHS) ✅
Equation: Cl₂ + 2ē → 2Cl⁻ (–2 charge LHS = –2 charge RHS) ✅
⚡ Convert to basic medium: Since there is no H⁺, we do not add OH⁻. 💧
💧 Reduction 2ē × 5 = 10ē ➡️ 5Cl₂ + 10ē → 10Cl⁻
Simplify: 3Cl₂ + 6OH⁻ → ClO₃⁻ + 5Cl⁻ + 3H₂O (–6 charge LHS = –6 charge RHS) ✅
✨ Final Balanced Equation (basic medium): 3Cl₂ + 6OH⁻ → ClO₃⁻ + 5Cl⁻ + 3H₂O ✅🌟
Reduction: It is the process in which electrons are gained by an atom or ion.
Oxidizing agent: It is a substance which gains electrons during a redox reaction from other substance thereby oxidizing it.
Reducing agent: It is a substance which loses electrons during a redox reaction giving to the other for reduction.
Redox reactions: These are electron transfer reactions in which oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously.
| Equation | Oxidation | Reduction | Oxidant | Reductant |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (i) 2HCl + HNO₃ → NOCl + Cl₂ + 2H₂O | Cl | N | N (HNO₃) | Cl (HCl) |
| (ii) Mg + H₂SO₄ → MgSO₄ + H₂ | Mg | S | Mg | S (H₂SO₄) |
| (iii) Fe₂O₃ + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO₂ | Fe | C | Fe (Fe₂O₃) | C (CO) |
| (iv) PCl₃ + 3H₂O → 3HCl + H₃PO₃ | None | None | None | None |
| (v) PCl₅ + 3H₂O → 5HCl + H₃PO₄ | None | None | None | None |
| (vi) 2Na + S → Na₂S | Na | S | S | Na |
| (vii) H₂S + Cl₂ → 2HCl + S | S | Cl | Cl (Cl₂) | S (H₂S) |
| (viii) HgCl₂ + 2KI → HgI₂ + 2KCl | None | None | None | None |
| (ix) H₂S + Br₂ → 2HBr + S | S | Br | Br (Br₂) | S (H₂S) |
| (x) 2Li + S → Li₂S | Li | S | S | Li |
💥 جونؔ ایلیا 🎯 💥
💔 صرف زندہ رہے ہم تو مر جائیں گے
🌌 سب بچھڑ جائیں گے سب بکھر جائیں گے
🌅 صبح ہوتے ہی سب کام پر جائیں گے
⚡ کیا ستم ہے کہ ہم لوگ مر جائیں گے
🕊️ بے خبر آئے ہیں بے خبر جائیں گے
🔥 جونؔ ایلیا ۔ غزل 🔥
🕊️ ہر طرف ہو رہی ہے یہی گفتگو، تم کہاں جاؤ گے ہم کہاں جائیں گے
⏳ وقت کی اس مسافت میں بے آرزو، تم کہاں جاؤ گے ہم کہاں جائیں گے
🌌 ہیں یہ سرگوشیاں دربدر کوبکو، تم کہاں جاؤ گے ہم کہاں جائیں گے
💔 تھا سراب اپنا سرمایۂِ جستجو، تم کہاں جاؤ گے ہم کہاں جائیں گے
🌙 بس گزرنے کو ہے موسمِ ہائے و ہُو، تم کہاں جاؤ گے ہم کہاں جائیں گے
🌹 گُل زمیں سے ابلنے کو ہے اب لہو، تم کہاں جاؤ گے ہم کہاں جائیں گے؟
🍷 آخرِ شب ہے خالی ہیں جام و سُبو، تم کہاں جاؤ گے ہم کہاں جائیں گے؟
🔥 بس گزرنے کو ہے موسمِ ہاؤ و ہُو، تم کہاں جاؤ گے ہم کہاں جائیں گے؟
💥 غزل ۔۔۔۔ جونؔ ایلیا 💥
💭 جانے کیسے لوگ وہ ہوں گے جو اس کو بھاتے ہوں گے
🔥 میرے بجھنے کا نظارہ کرنے آ جاتے ہوں گے
💔 آنے والوں سے کیا مطلب آتے ہیں آتے ہوں گے
🌌 یوں ہی میرے بال ہیں بکھرے اور بکھر جاتے ہوں گے
💔 وہ جو سمٹتے ہوں گے ان میں وہ تو مر جاتے ہوں گے
🌙 یعنی میرے بعد بھی یعنی سانس لیے جاتے ہوں گے
💥 غزل ۔۔۔۔ جونؔ ایلیا 💥
💭 ہر لمحہ جی رہے ہیں مگر خیریت سے ہیں
🌌 دشتِ گماں کے خاک بسر خیریت سے ہیں
🕊️ اللہ اور تمام بشر خیریت سے ہیں
💧 مژگانِ خشک و دامنِ تر خیریت سے ہیں
🌟 یعنی تمام اہلِ نظر خیریت سے ہیں
🔥 سودائیانِ حال کے سر خیریت سے ہیں
💭 شکوے کی بات ہے، وہ اگر خیریت سے ہیں
🏚️ خاک اڑ رہی ہے اور کھنڈر خیریت سے ہیں
✨ جونؔ! ایک معجزہ ہے اگر خیریت سے ہیں
📜 اور اپنے صاحبانِ ہنر خیریت سے ہیں
⚔️ برگستوان و تیغ و تبر خیریت سے ہیں
🚪 بس در ہے اور بندئہ در خیریت سے ہیں
📖 ورنہ تمام جوشؔ و جگرؔ خیریت سے ہیں
🌙 باقی جو ہیں وہ شام و سحر خیریت سے ہیں
💥 غزل ۔۔۔۔ جونؔ ایلیا 💥
☀️ دھوپ آنگن میں پھیل جاتی ہے
🌆 شہر کوچوں میں خاک اڑاتی ہے
🕰️ میز پر گرد جمتی جاتی ہے
🌙 اب کسے رات بھر جگاتی ہے
💔 بے دلی بھی تو لب ہلاتی ہے
🌸 زندگی خواب کیوں دکھاتی ہے
💭 خواہشِ غیر کیوں ستاتی ہے
😮 ہمنشیں! سانس پھول جاتی ہے
👀 غور کرنے پہ یاد آتی ہے
💔 روز ایک چیز ٹوٹ جاتی ہے
💥 غزل ۔۔۔۔ جونؔ ایلیا 💥
💭 یہ دل کے خواب کی صورت نہ رائیگاں جائے
🌌 یہ شہر شہر کی محنت نہ رائیگاں جائے
💡 یہ خود سے اپنی رفاقت نہ رائیگاں جائے
🌙 کہیں یہ حسنِ طبیعت نہ رائیگاں جائے
💔 ہمارا عہدِ محبت نہ رائیگاں جائے
✨ یہ اجتماع یہ صحبت نہ رائیگاں جائے
🌟 رہے خیال یہ مہلت نہ رائیگاں جائے
🔥 تیرے جنون کی حالت نہ رائیگاں جائے
💥 غزل ۔۔۔۔ جونؔ ایلیا 💥
💭 شوق اس کا کمال ہے، تاحال
😔 جی ہمارا نڈھال ہے، تاحال
⚡ شوقِ بحث و جدال ہے، تاحال
❓ ہر جواب اک سوال ہے، تاحال
💔 دل میں زخمِ کمال ہے، تاحال
🌟 ذہن میں اک مثال ہے، تاحال
🌿 ہوسِ اندمال ہے، تاحال
🌸 آپ اپنی مثال ہے، تاحال
💔 بے امیدِ وصال ہے، تاحال
🌙 وہ جو تھا اک ملال ہے، تاحال
🎨 رنگ بے خدوخال ہے، تاحال
🦌 تو غزل کا غزال ہے، تاحال
💭 تجھ کو پانا محال ہے، تاحال
😔 پر وہی میرا حال ہے، تاحال
💥 غزل ۔۔۔۔ جونؔ ایلیا 💥
🌙 ہم ہیں حیران اپنی حیرت کے
💔 تم نہیں تھے مری طبیعت کے
🌟 کیا عجب عیش تھے شکایت کے
🎁 یہ عطیے ہیں دل کی عادت کے
⚖️ ہم ہی مفتی ہیں اہلسنت کے
🛠️ نہیں خوگر کسی مشقت کے
🌙 ہیں یہ لمحے تمام ہجرت کے
📖 ہیں عجب معجزے حکایت کے
💥 غزل ۔۔۔۔ جونؔ ایلیا 💥
💔 خود کو ہلاک کر لیا، خود کو فدا نہیں کیا
😔 تو نے تو ہم سے آج تک کوئی گلہ نہیں کیا
📜 میں نے بھی ایک شخص کا قرض ادا نہیں کیا
🌟 آپ بہت شریف ہیں، آپ نے کیا نہیں کیا
🙏 ہم نے نہیں کیا وہ کام، ہاں باخُدا نہیں کیا
💡 اُس نے تو کارِ جہل بھی بے علما نہیں کیا
💥 غزل ۔۔۔۔ جونؔ ایلیا 💥
🌙 تھا تو اک شہر خاکساروں کا
😔 اب پتہ کیا ہے دل فگاروں کا
🛏️ بسترا اب کہاں ہے یاروں کا
🕊️ کون پُرساں ہے یادگاروں کا
🌌 مجھ سے کیا ذکر رہ گزاروں کا
🌟 عیش مت پوچھ دعویداروں کا
🐎 نہ پیادوں کا نہ سواروں کا
📚 دہر ہے صرف استعاروں کا
🤝 کیا ہوا جانے جانثاروں کا
🌪️ ایک جلسہ تھا شعلہ خواروں کا
💥 حضرتِ جونؔ ایلیا 💥 🎨 خاتم الشعرا و شاعرِ بے مثل و بے بدل 🎨
🌙 اور ہم ہیں کہ نام کر رہے ہیں
✨ ہم جو یہ اہمتمام کررہے ہیں
🔥 آپ تو قتلِ عام کررہے ہیں
💭 ہم تو خود سے کلام کررہے ہیں
🤝 ہر کسی کو سلام کررہے ہیں
💔 اپنا ہونا حرام کررہے ہیں
📢 ہم یہ اعلانِ عام کررہے ہیں
🥂 ناف پیالے کو جام کررہے ہیں
🙏 اور وہ احترام کررہے ہیں
🌌 کوئے دل میں خرام کررہے ہیں
🕊️ بات ہی ہم تمام کررہے ہیں
🥁 بے سبب دھوم دھام کررہے ہیں
🗡️ تیغ کو بے نیام کررہے ہیں
⏳ دم کو بس دوام کررہے ہیں
🏛️ ہم ابد میں قیام کررہے ہیں
💥 حضرتِ جونؔ ایلیا 💥 🎨 خاتم الشعرا و شاعرِ بے مثل و بے بدل 🎨
💔 بچھڑنا ہے تو جھگڑا کیوں کریں ہم
🔥 کوئی ہنگامہ برپا کیوں کریں ہم
❌ پر اب اس باب کو وا کیوں کریں ہم
⚖️ بھلا گھاٹے کا سودا کیوں کریں ہم
🌟 تمہاری ہی تمنّا کیوں کریں ہم
📜 تو ساری عمر ایفا کیوں کریں ہم
🚶 فقط کمروں میں ٹہلا کیوں کریں ہم
💡 وہ سرمایہ اکٹھا کیوں کریں ہم
😔 تو پھر دنیا کی پروا کیوں کریں ہم
👀 بھلا اندھوں سے پردہ کیوں کریں ہم
🤝 سو خود پر بھی بھروسا کیوں کریں ہم
🍽️ تمہیں راتب مہیا کیوں کریں ہم
🌪️ زمیں کا بوجھ ہلکا کیوں کریں ہم
🕊️ یہاں کارِ مسیحا کیوں کریں ہم