













⭐MDCAT Turbo Summary of Isomerism & Types of Isomerism
✨ Master this high-yield topic in minutes!
🔬 What is Isomerism?
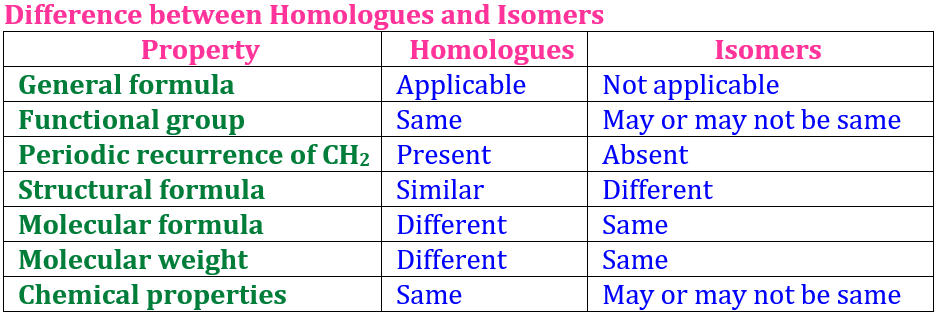
Isomerism refers to compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures or properties.
👉 Same formula, different arrangement = different behavior!
🧪 Importance in MDCAT:
-
Frequently tested 📝
-
Helps understand reactions, structures & properties
-
Key in Organic Chemistry scoring! 🔥
🧩 Main Types of Isomerism
1️⃣ Structural Isomerism (Constitutional Isomerism)
📌 Atoms connected differently
Different arrangement of bonds → different compounds.
🔹 Types:
-
Chain Isomerism 🌿
Different carbon chain arrangement.
-
Position Isomerism 📍
Functional group at different positions.
-
Functional Group Isomerism 🧪
Same formula, different functional groups.
-
Metamerism 🔗
Different alkyl groups on either side of functional group.
-
Tautomerism ↔️
Rapid interconversion between forms (e.g., keto–enol).
2️⃣ Stereoisomerism
📌 Same formula, same bonding, different spatial arrangement 🌀
🔹 Types:
-
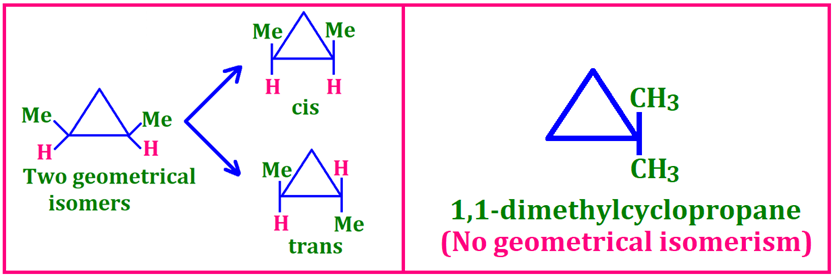
Geometrical (Cis–Trans) Isomerism 🔄
Restricted rotation (double bond or ring).
-
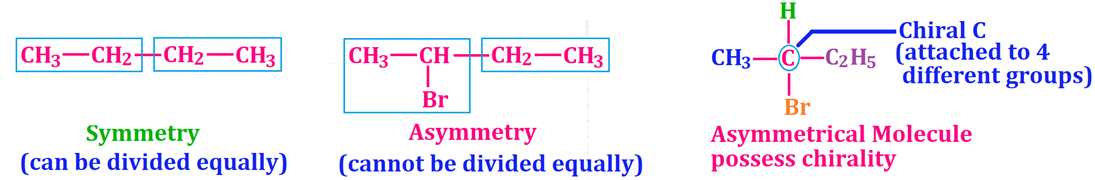
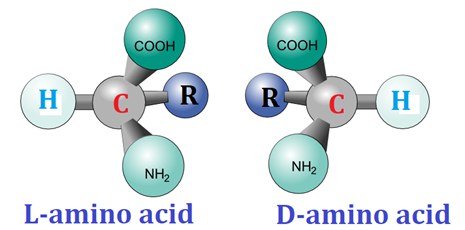
Optical Isomerism ✨
Chiral molecules, non-superimposable mirror images (enantiomers).
Rotate plane-polarized light → 🔦 (+) or (−)
🎯 Fast MDCAT Recall Tips
👉 Structural = bonding difference
👉 Stereo = 3D arrangement difference
👉 Geometrical = cis/trans
👉 Optical = chirality + rotation of light
👉 Tautomerism = dynamic equilibrium
🔥 One-Line Super Summary (MDCAT Hack)
“Isomers have the same formula but differ either in bonding (structural) or in 3D space (stereo).” 🧠⚡
📚 High-Yield Examples
-
Ethanol & Dimethyl ether → Functional group isomers
-
Butane & Isobutane → Chain isomers
-
Cis-2-butene & Trans-2-butene → Geometrical isomers
-
Lactic acid enantiomers → Optical isomers
💯 MDCAT Score Booster
✨ Practice past papers
✨ Draw structures to visualize
✨ Focus on functional group & stereo questions
✨ Remember examples — they guarantee quick marks!
📝 📚 MDCAT Quick Quiz — Isomerism (With Reasons)
Q1️⃣ Which pair represents functional group isomerism?
🟦 A. Ethanol & Dimethyl ether
🟩 B. Butane & Isobutane
🟨 C. Propanal & Propanone
🟧 D. Ethene & Ethyne
✅ Correct: A. Ethanol & Dimethyl ether
Reason: Same formula (C₂H₆O) but different functional groups: alcohol vs ether.
Q2️⃣ Tautomerism occurs due to:
🟦 A. Restricted rotation
🟩 B. Dynamic interconversion
🟨 C. Chirality
🟧 D. Ring strain
✅ Correct: B. Dynamic interconversion
Reason: Tautomers rapidly interconvert, like keto–enol forms.
Q3️⃣ Cis–trans isomerism is a type of:
🟦 A. Structural isomerism
🟩 B. Functional isomerism
🟨 C. Geometrical isomerism
🟧 D. Optical isomerism
✅ Correct: C. Geometrical isomerism
Reason: It arises due to restricted rotation around double bonds or rings.
Q4️⃣ Optical isomers differ in:
🟦 A. Molecular formula only
🟩 B. Rotation of plane-polarized light
🟨 C. Number of carbon atoms
🟧 D. Their boiling points only
✅ Correct: B. Rotation of plane-polarized light
Reason: Enantiomers rotate light in opposite directions (+/–).
Q5️⃣ Butane (C₄H₁₀) and Isobutane (C₄H₁₀) are:
🟦 A. Position isomers
🟩 B. Chain isomers
🟨 C. Optical isomers
🟧 D. Metamers
✅ Correct: B. Chain isomers
Reason: Same formula but different carbon chain branching.
Q6️⃣ Which is NOT a type of structural isomerism?
🟦 A. Chain
🟩 B. Position
🟨 C. Functional group
🟧 D. Optical
✅ Correct: D. Optical
Reason: Optical isomerism belongs to stereoisomerism, not structural.
Q7️⃣ Compounds with same connectivity but different 3D arrangement are:
🟦 A. Structural isomers
🟩 B. Stereoisomers
🟨 C. Functional isomers
🟧 D. Resonance structures
✅ Correct: B. Stereoisomers
Reason: Stereoisomers differ only in spatial arrangement.
Q8️⃣ Keto–enol interconversion is an example of:
🟦 A. Tautomerism
🟩 B. Position isomerism
🟨 C. Geometrical isomerism
🟧 D. Chain isomerism
✅ Correct: A. Tautomerism
Reason: It's a classic example of dynamic structural shifting.
Q9️⃣ Which condition is essential for geometrical (cis–trans) isomerism?
🟦 A. Presence of a chiral carbon
🟩 B. Free rotation around bond
🟨 C. Restricted rotation (C=C or ring)
🟧 D. Same functional group
✅ Correct: C. Restricted rotation (C=C or ring)
Reason: Geometrical isomers form only when rotation is restricted.
Q1️⃣0️⃣ Which pair shows position isomerism?
🟦 A. Propanol & Propanone
🟩 B. Ethylamine & Methylamine
🟨 C. 1-Propanol & 2-Propanol
🟧 D. Butane & Isobutane
✅ Correct: C. 1-Propanol & 2-Propanol
Reason: Same functional group (–OH), different positions on carbon chain.
Q1️⃣1️⃣ Compounds that differ only in the arrangement of alkyl groups around a functional group are:
🟦 A. Chain isomers
🟩 B. Metamers
🟨 C. Enantiomers
🟧 D. Functional isomers
✅ Correct: B. Metamers
Reason: Metamerism arises due to unequal alkyl groups on both sides of a functional group.
Q1️⃣2️⃣ Enantiomers have:
🟦 A. Identical physical properties except optical activity
🟩 B. Different molecular formula
🟨 C. Different boiling points
🟧 D. Different connectivity of atoms
✅ Correct: A. Identical physical properties except optical activity
Reason: Enantiomers differ only in the direction they rotate light.
Q1️⃣3️⃣ Which of the following compounds can show optical isomerism?
🟦 A. 2-Chlorobutane
🟩 B. Propene
🟨 C. But-1-ene
🟧 D. Carbon tetrachloride
✅ Correct: A. 2-Chlorobutane
Reason: It contains a chiral carbon (four different groups attached).
Q1️⃣4️⃣ Which pair represents chain isomerism?
🟦 A. Pentan-1-ol & Pentan-2-ol
🟩 B. Pentane & 2-methylbutane
🟨 C. Propanal & Propanone
🟧 D. Ethanol & Dimethyl ether
✅ Correct: B. Pentane & 2-methylbutane
Reason: Same formula, different carbon chain branching.
Q1️⃣5️⃣ Isomers that differ in the spatial arrangement around a chiral center are called:
🟦 A. Functional isomers
🟩 B. Chain isomers
🟨 C. Optical isomers
🟧 D. Metamers
✅ Correct: C. Optical isomers
Reason: Optical isomers exist due to chirality.
Q1️⃣6️⃣ A compound that shows cis–trans isomerism must have:
🟦 A. Two identical groups on one carbon
🟩 B. Two different groups on each carbon of C=C
🟨 C. A chiral center
🟧 D. A benzene ring
✅ Correct: B. Two different groups on each carbon of C=C
Reason: Necessary condition for geometrical isomerism.
Q1️⃣7️⃣ Which type of isomerism is shown by lactic acid enantiomers?
🟦 A. Geometrical
🟩 B. Optical
🟨 C. Chain
🟧 D. Position
✅ Correct: B. Optical
Reason: Lactic acid has a chiral carbon → exists as L- and D- forms.
Q1️⃣8️⃣ The pair CH₃OCH₃ and CH₃CH₂OH exhibits:
🟦 A. Chain isomerism
🟩 B. Metamerism
🟨 C. Functional group isomerism
🟧 D. Optical isomerism
✅ Correct: C. Functional group isomerism
Reason: Ether vs alcohol but same formula (C₂H₆O).
Q1️⃣9️⃣ Stereoisomers must have:
🟦 A. Different molecular formula
🟩 B. Same connectivity but different 3D arrangement
🟨 C. Different functional groups
🟧 D. Different numbers of atoms
✅ Correct: B. Same connectivity but different 3D arrangement
Reason: This is the definition of stereoisomerism.
Q2️⃣0️⃣ Which of the following is NOT stereoisomerism?
🟦 A. Optical isomerism
🟩 B. Geometrical isomerism
🟨 C. Cis–trans isomerism
🟧 D. Functional group isomerism
✅ Correct: D. Functional group isomerism
Reason: It belongs to structural isomerism, not stereo.
Q2️⃣1️⃣ Which of the following is a pair of stereoisomers?
🟦 A. Ethanol & Propanol
🟩 B. Cis-2-butene & Trans-2-butene
🟨 C. Propanal & Propanone
🟧 D. Butane & Isobutane
✅ Correct: B. Cis-2-butene & Trans-2-butene
Reason: They differ only in spatial arrangement → geometrical isomers → a type of stereoisomerism.
Q2️⃣2️⃣ Which compound CANNOT show optical isomerism?
🟦 A. 2-Butanol
🟩 B. 2-Chlorobutane
🟨 C. 2-Methylpropane
🟧 D. Lactic acid
✅ Correct: C. 2-Methylpropane
Reason: No carbon has four different groups → no chirality.
Q2️⃣3️⃣ Structural isomers have:
🟦 A. Different molecular formulas
🟩 B. Same formula, different bonding pattern
🟨 C. Same structure but rotated
🟧 D. Same physical properties
✅ Correct: B. Same formula, different bonding pattern
Reason: Bond connectivity changes → structural isomerism.
Q2️⃣4️⃣ Which pair shows position isomerism of a double bond?
🟦 A. But-1-ene & But-2-ene
🟩 B. Pentane & Isopentane
🟨 C. Propanol & Propanone
🟧 D. Ethanol & Methanol
✅ Correct: A. But-1-ene & But-2-ene
Reason: Same functional group (C=C), only the position changes.
Q2️⃣5️⃣ A pair that represents metamerism is:
🟦 A. CH₃OCH₃ & CH₃CH₂OH
🟩 B. C₂H₅–O–C₃H₇ & C₃H₇–O–C₂H₅
🟨 C. Pentane & Neopentane
🟧 D. But-1-ene & But-2-ene
✅ Correct: B. C₂H₅–O–C₃H₇ & C₃H₇–O–C₂H₅
Reason: Same functional group (ether) but different alkyl groups around it.
Q2️⃣6️⃣ Geometrical isomerism is NOT possible in:
🟦 A. 2-Butene
🟩 B. 1,2-Dichloroethene
🟨 C. Cyclohexane derivatives
🟧 D. Ethane
✅ Correct: D. Ethane
Reason: Free rotation around C–C single bond → no cis–trans isomers.
Q2️⃣7️⃣ Enantiomers differ in:
🟦 A. All physical properties
🟩 B. Only chemical properties
🟨 C. Direction of optical rotation
🟧 D. Functional groups
✅ Correct: C. Direction of optical rotation
Reason: Enantiomers rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions.
Q2️⃣8️⃣ Which of the following shows both geometrical and optical isomerism?
🟦 A. 2-Butene
🟩 B. 2-Chlorobutane
🟨 C. Tartaric acid
🟧 D. 2,3-Dichlorobutane
✅ Correct: D. 2,3-Dichlorobutane
Reason: Can have cis/trans arrangement and chiral centers (meso & enantiomers).
Q2️⃣9️⃣ The phenomenon where two compounds have the same molecular formula but different functional groups is:
🟦 A. Position isomerism
🟩 B. Functional group isomerism
🟨 C. Chain isomerism
🟧 D. Tautomerism
✅ Correct: B. Functional group isomerism
Reason: Example: ethanol & dimethyl ether.
Q3️⃣0️⃣ Which statement about tautomers is TRUE?
🟦 A. They are resonance structures
🟩 B. They differ only in 3D orientation
🟨 C. They are interconvertible isomers
🟧 D. They have different molecular formulas
✅ Correct: C. They are interconvertible isomers
Reason: Tautomers exist in dynamic equilibrium — NOT resonance structures, but real compounds.
Q3️⃣1️⃣ Which of the following exhibits maximum number of structural isomers?
🟦 A. C₄H₁₀
🟩 B. C₅H₁₂
🟨 C. C₆H₁₄
🟧 D. C₇H₁₆
✅ Correct: D. C₇H₁₆
Reason: More carbons → more ways to arrange chains.
Q3️⃣2️⃣ Compounds that have the same connectivity but differ by rotation around a single bond are:
🟦 A. Conformers
🟩 B. Tautomers
🟨 C. Enantiomers
🟧 D. Positional isomers
✅ Correct: A. Conformers
Reason: Conformations arise from rotation about C–C single bonds.
Q3️⃣3️⃣ Which pair represents diastereomers?
🟦 A. Cis-2-butene & Trans-2-butene
🟩 B. Lactic acid enantiomers
🟨 C. Butane & Isobutane
🟧 D. Propanal & Propanone
✅ Correct: A. Cis-2-butene & Trans-2-butene
Reason: Geometrical isomers are diastereomers (not mirror images).
Q3️⃣4️⃣ A compound must have which feature to show optical activity without chirality?
🟦 A. Internal mirror plane
🟩 B. Restricted rotation
🟨 C. Helical or axial chirality
🟧 D. Double bond
✅ Correct: C. Helical or axial chirality
Reason: Some molecules are chiral due to shape (e.g., allenes) even without chiral carbon.
Q3️⃣5️⃣ 2,3-dibromobutane has how many stereoisomers?
🟦 A. 2
🟩 B. 3
🟨 C. 4
🟧 D. 5
✅ Correct: B. 3
Reason: Two chiral centers → 4 possible, but one is meso, so total = 3.
Q3️⃣6️⃣ Which compound may exhibit meso behavior?
🟦 A. 2-Chlorobutane
🟩 B. 2,3-Dichlorobutane
🟨 C. 1,2-Dichloroethane
🟧 D. But-2-yne
✅ Correct: B. 2,3-Dichlorobutane
Reason: Symmetry + multiple chiral centers → meso structure possible.
Q3️⃣7️⃣ Optical isomerism is NOT shown by:
🟦 A. Allenes
🟩 B. Lactic acid
🟨 C. Glycine
🟧 D. Tartaric acid
✅ Correct: C. Glycine
Reason: Central carbon has two identical –H groups → no chirality.
Q3️⃣8️⃣ Which is true for enantiomers?
🟦 A. Rotate light in same direction
🟩 B. Identical boiling/melting points
🟨 C. One is stable, other unstable
🟧 D. Have different molecular weights
✅ Correct: B. Identical boiling/melting points
Reason: Enantiomers have identical physical properties except optical rotation.
Q3️⃣9️⃣ Which is an example of conformational isomerism?
🟦 A. Gauche & Anti forms of butane
🟩 B. Cis-trans 2-butene
🟨 C. Keto & enol forms
🟧 D. Ethanol & ether
✅ Correct: A. Gauche & Anti forms of butane
Reason: Conformers differ by rotation around σ-bond.
Q4️⃣0️⃣ Which bond prevents free rotation leading to geometrical isomers?
🟦 A. C–C single
🟩 B. C=C double
🟨 C. C–H
🟧 D. N–H
✅ Correct: B. C=C double
Reason: π-bond restricts rotation.
Q4️⃣1️⃣ Meso compounds are:
🟦 A. Superimposable on mirror image
🟩 B. Always optically active
🟨 C. Enantiomer pairs
🟧 D. Functional isomers
✅ Correct: A. Superimposable on mirror image
Reason: Internal symmetry cancels chirality.
Q4️⃣2️⃣ Which CANNOT exhibit geometrical isomerism?
🟦 A. CH₂=CH₂
🟩 B. CHCl=CHCl
🟨 C. Cyclobutene
🟧 D. CH₃CH=CH₂
✅ Correct: A. CH₂=CH₂
Reason: Each carbon lacks two different groups → no cis/trans.
Q4️⃣3️⃣ Maximum number of stereoisomers for a molecule with n chiral centers (no meso forms) is:
🟦 A. 2ⁿ
🟩 B. n²
🟨 C. 2n
🟧 D. n!
✅ Correct: A. 2ⁿ
Reason: Each center independently gives R/S options.
Q4️⃣4️⃣ Compounds showing interconversion by proton shift are:
🟦 A. Conformers
🟩 B. Tautomers
🟨 C. Enantiomers
🟧 D. Diastereomers
✅ Correct: B. Tautomers
Reason: Classic example: keto–enol.
Q4️⃣5️⃣ Which of the following must have a chiral center?
🟦 A. Racemic mixtures
🟩 B. Meso compounds
🟨 C. Enantiomers
🟧 D. Cis/trans isomers
✅ Correct: C. Enantiomers
Reason: Enantiomers = mirror-image chiral molecules.
Q4️⃣6️⃣ A racemic mixture is:
🟦 A. Optically active
🟩 B. 50:50 mixture of enantiomers
🟨 C. A type of chain isomer
🟧 D. Always meso
✅ Correct: B. 50:50 mixture of enantiomers
Reason: Equal + and – rotations cancel → optical inactivity.
Q4️⃣7️⃣ Which of the following can exhibit axial chirality?
🟦 A. Alkanes
🟩 B. Disubstituted biphenyls
🟨 C. Straight-chain alkenes
🟧 D. Saturated hydrocarbons
✅ Correct: B. Disubstituted biphenyls
Reason: Restricted rotation around the axis → axial chirality.
Q4️⃣8️⃣ Which statement about diastereomers is TRUE?
🟦 A. They have identical physical properties
🟩 B. They are non-superimposable mirror images
🟨 C. They differ in physical properties
🟧 D. They rotate light equally and opposite
✅ Correct: C. They differ in physical properties
Reason: Diastereomers behave differently (boiling point, solubility, etc.).
Q4️⃣9️⃣ Identify the pair showing functional group isomerism:
🟦 A. Propanone & Propanal
🟩 B. Butane & Isobutane
🟨 C. Ethene & Cycloethane
🟧 D. Lactic acid enantiomers
✅ Correct: A. Propanone & Propanal
Reason: Ketone ⇆ aldehyde = functional group difference.
Q5️⃣0️⃣ The number of structural isomers of C₆H₁₄ (hexane) is:
🟦 A. 3
🟩 B. 4
🟨 C. 5
🟧 D. 6
✅ Correct: C. 5
Reason: Hexane has five possible chain arrangements.
Q5️⃣1️⃣ Which of the following compounds can show both axial and central chirality?
🟦 A. 2-Butanol
🟩 B. Disubstituted biphenyl with bulky groups
🟨 C. Methanol
🟧 D. Propylamine
✅ Correct: B. Disubstituted biphenyl with bulky groups
Reason: Restricted rotation + possible chiral center → both types of chirality.
Q5️⃣2️⃣ Allenes show optical isomerism when:
🟦 A. Both terminal carbons have identical groups
🟩 B. The central carbon is chiral
🟨 C. The two terminal carbons have different groups
🟧 D. The molecule has a cis/trans bond
✅ Correct: C. The two terminal carbons have different groups
Reason: Asymmetry causes axial chirality.
Q5️⃣3️⃣ Which molecule can have maximum stereoisomers?
🟦 A. A molecule with 1 chiral center
🟩 B. A molecule with 2 chiral centers + symmetry
🟨 C. A molecule with 4 chiral centers (no symmetry)
🟧 D. A meso compound
✅ Correct: C. A molecule with 4 chiral centers (no symmetry)
Reason: 2⁴ = 16 stereoisomers (max).
Q5️⃣4️⃣ Which is TRUE about meso compounds?
🟦 A. They rotate plane-polarized light
🟩 B. They contain chiral centers but are achiral overall
🟨 C. They always have an enantiomer
🟧 D. They exist only in alkenes
✅ Correct: B. They contain chiral centers but are achiral overall
Reason: Internal symmetry neutralizes optical activity.
Q5️⃣5️⃣ Which stereoisomeric relationship is found in cis-1,2-dimethylcyclohexane vs trans-1,2-dimethylcyclohexane?
🟦 A. Enantiomers
🟩 B. Diastereomers
🟨 C. Meso pair
🟧 D. Chain isomers
✅ Correct: B. Diastereomers
Reason: Non-mirror image stereoisomers.
Q5️⃣6️⃣ 1,3-dichloropropene shows geometrical isomerism due to:
🟦 A. Chiral center
🟩 B. Restricted rotation around double bond
🟨 C. Tautomerism
🟧 D. Resonance
✅ Correct: B. Restricted rotation around double bond
Reason: Classic cis/trans due to C=C.
Q5️⃣7️⃣ Which of the following is a pair of conformers?
🟦 A. Enol & keto forms
🟩 B. Chair & boat forms of cyclohexane
🟨 C. Cis-2-butene & trans-2-butene
🟧 D. Lactic acid enantiomers
✅ Correct: B. Chair & boat forms of cyclohexane
Reason: Interconvert via rotation (conformational).
Q5️⃣8️⃣ Which pair represents enantiomers?
🟦 A. Non-superimposable mirror images
🟩 B. Superimposable mirror images
🟨 C. Same boiling point but opposite solubility
🟧 D. Differ only in bond connectivity
✅ Correct: A. Non-superimposable mirror images
Reason: Core definition of enantiomers.
Q5️⃣9️⃣ For a molecule with 2 chiral centers, how many diastereomers exist (no meso)?
🟦 A. 0
🟩 B. 1
🟨 C. 2
🟧 D. 4
✅ Correct: C. 2
Reason: Total stereoisomers = 4 (RR, SS, RS, SR), enantiomer pairs = 2 → diastereomers = 2.
Q6️⃣0️⃣ Which of the following shows geometrical isomerism in rings?
🟦 A. Cyclohexane
🟩 B. Cyclopropane
🟨 C. 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane
🟧 D. Benzene
✅ Correct: C. 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane
Reason: Restricted rotation in ring → cis/trans.
Q6️⃣1️⃣ Which compound can exist as a meso form?
🟦 A. 2,2-dichlorobutane
🟩 B. 3,4-dibromopentane (with symmetry)
🟨 C. Propanal
🟧 D. 1-butyne
✅ Correct: B. 3,4-dibromopentane
Reason: Middle symmetry + two chiral centers → meso possible.
Q6️⃣2️⃣ A pair of compounds differing only in configuration is called:
🟦 A. Enantiomers/diastereomers
🟩 B. Conformers
🟨 C. Rotamers
🟧 D. Constitutional isomers
✅ Correct: A. Enantiomers/diastereomers
Reason: Configuration = fixed 3D arrangement.
Q6️⃣3️⃣ Which statement about racemic mixtures is FALSE?
🟦 A. They are optically inactive
🟩 B. They contain equal R and S forms
🟨 C. They have different physical properties than pure enantiomers
🟧 D. They rotate light strongly
✅ Correct: D. They rotate light strongly
Reason: They show zero optical rotation.
Q6️⃣4️⃣ Alkynes show geometrical isomerism when:
🟦 A. One sp carbon has four different groups
🟩 B. Both sp carbons have different groups
🟨 C. They never show geometrical isomerism
🟧 D. Triple bond becomes partially double
✅ Correct: C. They never show geometrical isomerism
Reason: Linear geometry → no cis/trans.
Q6️⃣5️⃣ Which molecule exhibits planar chirality?
🟦 A. Cyclopropane
🟩 B. Ferrocenes with substituted rings
🟨 C. Ethane
🟧 D. Acetaldehyde
✅ Correct: B. Ferrocenes with substituted rings
Reason: Unequal substitution causes planar chirality.
Q6️⃣6️⃣ Which relationship is shown by R,S and R,R forms of a stereoisomer?
🟦 A. Enantiomers
🟩 B. Diastereomers
🟨 C. Conformers
🟧 D. Structural isomers
✅ Correct: B. Diastereomers
Reason: Not mirror images.
Q6️⃣7️⃣ How many optically active stereoisomers does 2,3-butanediol have?
🟦 A. 1
🟩 B. 2
🟨 C. 3
🟧 D. 4
✅ Correct: B. 2
Reason: Total = 3, but meso is inactive → 2 active.
Q6️⃣8️⃣ Isomerism caused by difference in position of double bond is:
🟦 A. Chain isomerism
🟩 B. Position isomerism
🟨 C. Stereo isomerism
🟧 D. Tautomerism
✅ Correct: B. Position isomerism
Reason: Functional group same, shift in location.
Q6️⃣9️⃣ Which pair is not isomers?
🟦 A. Ethane & propane
🟩 B. Ethanol & dimethyl ether
🟨 C. Pentane & neopentane
🟧 D. Propanal & propanone
✅ Correct: A. Ethane & propane
Reason: Different molecular formula → not isomers.
Q7️⃣0️⃣ Compounds that differ in arrangement around double bond are:
🟦 A. Conformers
🟩 B. Geometrical isomers
🟨 C. Enantiomers
🟧 D. Metamers
✅ Correct: B. Geometrical isomers
Reason: Cis/trans arrangement.
Q7️⃣1️⃣ Stereoisomers that are mirror images are:
🟦 A. Enantiomers
🟩 B. Diastereomers
🟨 C. Anomers
🟧 D. Rotamers
✅ Correct: A. Enantiomers
Reason: Non-superimposable mirror images.
Q7️⃣2️⃣ Which of the following is NOT a structural isomer?
🟦 A. Metamers
🟩 B. Chain isomers
🟨 C. Position isomers
🟧 D. Enantiomers
✅ Correct: D. Enantiomers
Reason: Enantiomers are stereoisomers.
Q7️⃣3️⃣ Which is true regarding diastereomers?
🟦 A. They are always mirror images
🟩 B. They have different physical properties
🟨 C. They rotate plane-polarized light equally
🟧 D. They have different molecular formulas
✅ Correct: B. They have different physical properties
Reason: Unlike enantiomers.
Q7️⃣4️⃣ Which of the following shows linkage isomerism?
🟦 A. NO₂⁻ ion coordinated as N or O donor
🟩 B. CH₃CH₂OH
🟨 C. CH₄
🟧 D. CCl₄
✅ Correct: A. NO₂⁻ ion coordinated as N or O donor
Reason: Coordination isomers in complex ions.
Q7️⃣5️⃣ Which type of isomerism arises due to ambidentate ligands?
🟦 A. Optical isomerism
🟩 B. Geometrical isomerism
🟨 C. Linkage isomerism
🟧 D. Chain isomerism
✅ Correct: C. Linkage isomerism
Reason: Same ligand binds through different atoms.
Q7️⃣6️⃣ Which type of isomerism is shown when a ligand in a coordination compound exchanges between inside and outside the coordination sphere?
🟦 A. Ionization isomerism
🟩 B. Linkage isomerism
🟨 C. Hydrate isomerism
🟧 D. Coordination isomerism
✅ Correct: A. Ionization isomerism
Reason: Example: [Co(NH₃)₅Br]SO₄ ↔ [Co(NH₃)₅SO₄]Br.
Q7️⃣7️⃣ Which molecule shows geometrical isomerism in octahedral complexes?
🟦 A. [Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺
🟩 B. [Pt(NH₃)₂Cl₂]
🟨 C. [Co(NH₃)₄Cl₂]⁺
🟧 D. [Ni(CN)₄]²⁻
✅ Correct: C. [Co(NH₃)₄Cl₂]⁺
Reason: Octahedral with MA₄B₂ shows cis/trans.
Q7️⃣8️⃣ Which of the following shows optical isomerism in coordination compounds?
🟦 A. Square planar complexes
🟩 B. Tetrahedral complexes with all identical ligands
🟨 C. Octahedral complexes of type M(AA)₃
🟧 D. Linear complexes
✅ Correct: C. M(AA)₃ (tris-chelates)
Reason: Tris-bidentate complexes are chiral.
Q7️⃣9️⃣ Which isomerism arises in complexes containing bidentate ligands?
🟦 A. Linkage isomerism
🟩 B. Geometrical & optical isomerism
🟨 C. Chain isomerism
🟧 D. Position isomerism
✅ Correct: B. Geometrical & optical isomerism
Reason: Chelation locks spatial arrangement → chirality possible.
Q8️⃣0️⃣ How many stereoisomers are possible for 2,3,4-trichloropentane (three chiral centers, no symmetry)?
🟦 A. 4
🟩 B. 6
🟨 C. 8
🟧 D. 16
✅ Correct: C. 8
Reason: 2³ = 8 stereoisomers.
Q8️⃣1️⃣ Which does NOT affect optical rotation?
🟦 A. Path length
🟩 B. Temperature
🟨 C. Solvent
🟧 D. Molecular weight
✅ Correct: D. Molecular weight
Reason: Optical rotation depends on concentration & environment, not mass.
Q8️⃣2️⃣ A molecule with two chiral centers and a plane of symmetry will have:
🟦 A. 4 stereoisomers
🟩 B. 3 stereoisomers
🟨 C. 2 stereoisomers
🟧 D. Only one stereoisomer
✅ Correct: B. 3 stereoisomers
Reason: One is meso (achiral) + one enantiomeric pair = 3.
Q8️⃣3️⃣ Allenes are optically active due to:
🟦 A. Chiral center
🟩 B. Axial chirality
🟨 C. Cis/trans double bond
🟧 D. Tautomerism
✅ Correct: B. Axial chirality
Reason: Orthogonal π-bonds create chirality without a chiral carbon.
Q8️⃣4️⃣ Which of the following shows conformational enantiomerism?
🟦 A. Hydrogen peroxide
🟩 B. Ethane
🟨 C. Cyclohexane
🟧 D. Biphenyls with bulky ortho groups
✅ Correct: D. Biphenyls with bulky ortho groups
Reason: Restricted rotation freezes chiral conformations.
Q8️⃣5️⃣ The relationship between cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane and trans-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane is:
🟦 A. Enantiomers
🟩 B. Diastereomers
🟨 C. Identical compounds
🟧 D. Conformers
✅ Correct: B. Diastereomers
Reason: Stereoisomers, not mirror images.
Q8️⃣6️⃣ The complex [Cr(en)₃]³⁺ shows:
🟦 A. Only cis/trans
🟩 B. Only linkage isomers
🟨 C. Optical isomerism
🟧 D. No isomerism
✅ Correct: C. Optical isomerism
Reason: Tris-chelates = chiral Λ and Δ forms.
Q8️⃣7️⃣ Which type of isomerism occurs when ligand and counter ion exchange?
🟦 A. Ionization isomerism
🟩 B. Linkage isomerism
🟨 C. Polymerization isomerism
🟧 D. Coordination position isomerism
✅ Correct: A. Ionization isomerism
Reason: Swap inside/outside coordination sphere.
Q8️⃣8️⃣ Which carbonyl complex shows linkage isomerism?
🟦 A. [Fe(CO)₅]
🟩 B. [Ni(CO)₄]
🟨 C. [M(CO)₄(NO)]
🟧 D. [Mn(CO)₅Cl]
✅ Correct: C. [M(CO)₄(NO)]
Reason: NO can bind through N or O (ambidentate ligand).
Q8️⃣9️⃣ Which pair of molecules can be separated by polarimetry?
🟦 A. Enantiomers
🟩 B. Chain isomers
🟨 C. Position isomers
🟧 D. Functional isomers
✅ Correct: A. Enantiomers
Reason: Only enantiomers rotate light differently.
Q9️⃣0️⃣ If a molecule has 4 chiral centers and also a plane of symmetry, how many stereoisomers exist?
🟦 A. 8
🟩 B. 10
🟨 C. 16
🟧 D. 15
✅ Correct: A. 8
Reason: Symmetry reduces from 16 → 8.
Q9️⃣1️⃣ Which of the following molecules can exhibit E/Z isomerism?
🟦 A. CH₂=CH₂
🟩 B. CH₃CH=CHCl
🟨 C. CHCl=CHCl
🟧 D. Both B and C
✅ Correct: D. Both B and C
Reason: Each C of double bond must have two different substituents.
Q9️⃣2️⃣ Which is not a stereochemical requirement for chirality?
🟦 A. No internal plane of symmetry
🟩 B. Molecule must be asymmetrical
🟨 C. At least one isotopic substitution
🟧 D. Non-superimposable mirror image
✅ Correct: C. At least one isotopic substitution
Reason: Chirality does not require isotopes.
Q9️⃣3️⃣ Which stereoisomerism is possible in square planar complexes like Pt(II)?
🟦 A. Optical
🟩 B. Conformational
🟨 C. Geometrical
🟧 D. Chain
✅ Correct: C. Geometrical
Reason: Square planar MA₂B₂ shows cis/trans.
Q9️⃣4️⃣ The complex [PtCl₂(NH₃)₂] shows:
🟦 A. Optical isomerism
🟩 B. Geometrical isomerism
🟨 C. Ionization isomerism
🟧 D. Linkage isomerism
✅ Correct: B. Geometrical isomerism
Reason: Classic cisplatin/transplatin.
Q9️⃣5️⃣ Which molecule will show no optical activity even though it has chiral centers?
🟦 A. meso-tartaric acid
🟩 B. lactic acid
🟨 C. alanine
🟧 D. 2-butanol
✅ Correct: A. meso-tartaric acid
Reason: Internal symmetry cancels chirality.
Q9️⃣6️⃣ Rotamers arise due to:
🟦 A. Restricted rotation around C=C
🟩 B. Free rotation around C–C bond
🟨 C. Bond cleavage
🟧 D. Chirality at multiple sites
✅ Correct: B. Free rotation around C–C bond
Reason: Rotational isomerism.
Q9️⃣7️⃣ Which isomerism is observed when complex ions swap ligands between them?
🟦 A. Ionization
🟩 B. Coordination
🟨 C. Linkage
🟧 D. Hydrate
✅ Correct: B. Coordination isomerism
Reason: Ligands exchange between metal centers.
Q9️⃣8️⃣ Which type of isomerism occurs in [Co(NH₃)₅(H₂O)]Cl₃ vs [Co(NH₃)₅Cl]Cl₂·H₂O?
🟦 A. Geometrical
🟩 B. Hydrate isomerism
🟨 C. Optical
🟧 D. Linkage
✅ Correct: B. Hydrate isomerism
Reason: Water inside vs outside coordination sphere.
Q9️⃣9️⃣ A compound shows optical activity even without a chiral carbon. This is due to:
🟦 A. Resonance
🟩 B. Tautomerism
🟨 C. Axial/planar chirality
🟧 D. Linkage isomerism
✅ Correct: C. Axial/planar chirality
Reason: Allens, biphenyls, ferrocenes show this.
Q1️⃣0️⃣0️⃣ Which pair represents not isomers but identical molecules?
🟦 A. Gauche & anti forms
🟩 B. Two resonance structures
🟨 C. R,R & S,S forms
🟧 D. Enantiomeric pair
✅ Correct: B. Two resonance structures
Reason: Resonance forms aren't real isomers — same molecule.
Q1️⃣0️⃣1️⃣ Which of the following pairs represents functional group isomerism?
🟦 A. CH₃COOH & HCOOCH₃
🟩 B. CH₃OCH₃ & C₂H₅OH
🟨 C. CH₃–CH₂–CHO & CH₃–CO–CH₃
🟧 D. All of the above
✅ Correct: D. All of the above
Reason: Acid–ester, ether–alcohol, aldehyde–ketone → functional group changes.
Q1️⃣0️⃣2️⃣ Maximum structural isomers are possible for which formula?
🟦 A. C₅H₁₂
🟩 B. C₆H₁₄
🟨 C. C₇H₁₆
🟧 D. C₈H₁₈
✅ Correct: D. C₈H₁₈
Reason: Higher carbon number → exponential rise in chain isomers.
Q1️⃣0️⃣3️⃣ Which molecule can exhibit chirality without a chiral center?
🟦 A. 2-Butanol
🟩 B. Allenes with different substituents
🟨 C. Cyclohexane
🟧 D. Propanone
✅ Correct: B. Allenes
Reason: Orthogonal π-bonds → axial chirality.
Q1️⃣0️⃣4️⃣ Which of the following shows geometrical isomerism?
🟦 A. CH₂=C(CH₃)₂
🟩 B. CH₃CH=CHCl
🟨 C. CH₂=CHCl
🟧 D. CH₃–C≡C–CH₃
✅ Correct: B. CH₃CH=CHCl
Reason: Both C’s of double bond have two different groups.
Q1️⃣0️⃣5️⃣ Which pair represents diastereomers?
🟦 A. Meso-tartaric acid & D-tartaric acid
🟩 B. Enantiomers of lactic acid
🟨 C. Conformers of ethane
🟧 D. Resonance structures of benzene
✅ Correct: A. Meso & D-tartaric acid
Reason: Stereoisomers not mirror images.
Q1️⃣0️⃣6️⃣ A compound showing keto–enol tautomerism represents which isomerism?
🟦 A. Functional
🟩 B. Structural
🟨 C. Dynamic
🟧 D. All of the above
✅ Correct: D. All of the above
Reason: Keto ⇆ enol differs in structure, function, and equilibrium.
Q1️⃣0️⃣7️⃣ Which exhibits optical activity in a racemic mixture after crystallization?
🟦 A. All racemates
🟩 B. Those that undergo spontaneous resolution
🟨 C. All enantiomeric pairs
🟧 D. Only meso compounds
✅ Correct: B. Spontaneous resolution
Reason: Certain racemates separate into pure enantiomer crystals.
Q1️⃣0️⃣8️⃣ Which hydrocarbon C₅H₁₀ shows both chain and geometrical isomerism?
🟦 A. 2-methyl-1-butene
🟩 B. Cyclopentane
🟨 C. 2-pentene
🟧 D. 1-pentene
✅ Correct: C. 2-pentene
Reason: Chain isomers exist + cis/trans in 2-pentene.
Q1️⃣0️⃣9️⃣ Cis/trans isomerism cannot occur in:
🟦 A. Cyclic compounds
🟩 B. Alkynes
🟨 C. Alkenes
🟧 D. Substituted cycloalkanes
✅ Correct: B. Alkynes
Reason: Linear geometry → no cis/trans.
Q1️⃣1️⃣0️⃣ The ratio of enantiomers in a mixture can be determined by:
🟦 A. UV spectroscopy
🟩 B. Polarimetry
🟨 C. Mass spectrometry
🟧 D. IR spectroscopy
✅ Correct: B. Polarimetry
Reason: Optical rotation reveals proportions.
Q1️⃣1️⃣1️⃣ The number of stereoisomers possible for 2,3-dichloropentane (two chiral centers, no symmetry):
🟦 A. 2
🟩 B. 3
🟨 C. 4
🟧 D. 8
✅ Correct: C. 4
Reason: 2² = 4; no meso form.
Q1️⃣1️⃣2️⃣ The relationship between gauche-butane and anti-butane is:
🟦 A. Geometrical isomers
🟩 B. Conformational isomers
🟨 C. Diastereomers
🟧 D. Functional isomers
✅ Correct: B. Conformational isomers
Reason: Differ by rotation around C–C bond.
Q1️⃣1️⃣3️⃣ Which pair is not a set of position isomers?
🟦 A. 1-propanol & 2-propanol
🟩 B. Nitrobenzene & m-nitrotoluene
🟨 C. But-1-ene & But-2-ene
🟧 D. 1-chloropropane & 2-chloropropane
✅ Correct: B. Nitrobenzene & m-nitrotoluene
Reason: Entire functional group changes (benzene vs toluene).
Q1️⃣1️⃣4️⃣ Which is true for enantiomers?
🟦 A. Same physical properties except optical rotation
🟩 B. Different boiling points
🟨 C. Same direction of rotation
🟧 D. Cannot exist in cyclic molecules
✅ Correct: A. Same physical properties except optical rotation
Reason: Classic enantiomer behavior.
Q1️⃣1️⃣5️⃣ A molecule with two chiral centers can still be achiral if:
🟦 A. It is cyclic
🟩 B. It has a plane of symmetry
🟨 C. It has no double bond
🟧 D. It contains nitrogen
✅ Correct: B. It has a plane of symmetry
Reason: Meso form.
Q1️⃣1️⃣6️⃣ Butanone and butanal are:
🟦 A. Functional isomers
🟩 B. Chain isomers
🟨 C. Metamers
🟧 D. Tautomers
✅ Correct: A. Functional isomers
Reason: Aldehyde vs ketone.
Q1️⃣1️⃣7️⃣ Which pair represents metamerism?
🟦 A. C₃H₈O ethers
🟩 B. C₄H₁₀ alkanes
🟨 C. CH₃COOH & HCOOH
🟧 D. CH₃NO₂ & CH₃ONO
✅ Correct: A. Ethers of formula C₃H₈O
Reason: Same functional group, different alkyl groups around it.
Q1️⃣1️⃣8️⃣ A racemic mixture becomes optically active when:
🟦 A. It is heated
🟩 B. One enantiomer is selectively destroyed
🟨 C. Concentration is doubled
🟧 D. Both enantiomers are present equally
✅ Correct: B. Selective destruction (“racemic resolution”)
Reason: Unequal enantiomers → net rotation.
Q1️⃣1️⃣9️⃣ The pair CH₃–CH₂–CH₂–OH and CH₃–CHOH–CH₃ are:
🟦 A. Chain isomers
🟩 B. Position isomers
🟨 C. Functional isomers
🟧 D. Not isomers
✅ Correct: C. Functional isomers
Reason: Primary alcohol vs secondary.
Q1️⃣2️⃣0️⃣ Which alkene C₄H₈ shows both cis/trans and optical isomerism?
🟦 A. 1-butene
🟩 B. 2-butene
🟨 C. 3-methyl-1-propene
🟧 D. 2-methylpropene
✅ Correct: B. 2-butene (cis/trans), BUT optical isomerism only in substituted versions
Reason: Cis/trans possible; substituted analogs can be chiral.
Q1️⃣2️⃣1️⃣ Which shows rotational (torsional) isomerism?
🟦 A. Biphenyl with free rotation
🟩 B. Alkanes
🟨 C. Cycloalkanes
🟧 D. Alkynes
✅ Correct: B. Alkanes
Reason: σ-bond rotation → conformers.
Q1️⃣2️⃣2️⃣ CH₃–CH₂–COOH and CH₃–O–CO–CH₃ are:
🟦 A. Functional isomers
🟩 B. Positional
🟨 C. Metamers
🟧 D. Geometrical
✅ Correct: A. Functional isomers
Reason: Acid vs ester.
Q1️⃣2️⃣3️⃣ Identify the isomers: CH₃–CH₂–CH₂–NH₂ and CH₃–CH(NH₂)–CH₃
🟦 A. Chain isomers
🟩 B. Metamers
🟨 C. Position isomers
🟧 D. Functional isomers
✅ Correct: C. Position isomers
Reason: Same carbon skeleton, –NH₂ position changes.
Q1️⃣2️⃣4️⃣ Hyperconjugation stabilizes which conformer of butane?
🟦 A. Fully eclipsed
🟩 B. Gauche
🟨 C. Anti
🟧 D. 60° eclipsed
✅ Correct: C. Anti
Reason: Steric repulsion minimized → most stable.
Q1️⃣2️⃣5️⃣ Which of the following is NOT a type of structural isomerism?
🟦 A. Chain
🟩 B. Conformational
🟨 C. Position
🟧 D. Functional
✅ Correct: B. Conformational
Reason: Conformations = stereoisomerism, not structural.
Q1️⃣2️⃣6️⃣ Which compound C₆H₁₂ exhibits both ring–chain isomerism and cis/trans isomerism?
🟦 A. Cyclohexane
🟩 B. Cyclopentane
🟨 C. Cyclobutane derivatives
🟧 D. 2-Hexene
✅ Correct: D. 2-Hexene
Reason: C₆H₁₂ → can be alkene (2-hexene, cis/trans) or cycloalkane.
Q1️⃣2️⃣7️⃣ A molecule shows optical activity but gives zero rotation in solution. Reason?
🟦 A. It is meso
🟩 B. Racemic mixture
🟨 C. Not chiral
🟧 D. Conformer interconversion
✅ Correct: B. Racemic mixture
Reason: Equal ± rotations cancel.
Q1️⃣2️⃣8️⃣ Which molecule shows planar chirality?
🟦 A. Ferrocene derivatives
🟩 B. 2-butanol
🟨 C. Cyclopentanol
🟧 D. Toluene
✅ Correct: A. Ferrocene derivatives
Reason: Sandwich structure → chiral plane.
Q1️⃣2️⃣9️⃣ Which of the following cannot exist as geometrical isomers?
🟦 A. CH₃–CH=CH–CH₃
🟩 B. CH₃–C(CH₃)=CH₂
🟨 C. CH₂=CCl₂
🟧 D. CH₃CH=CHCl
✅ Correct: B. CH₃–C(CH₃)=CH₂
Reason: One double-bond carbon has two identical groups.
Q1️⃣3️⃣0️⃣ But-2-ene and cyclobutane are examples of:
🟦 A. Functional isomers
🟩 B. Ring–chain isomers
🟨 C. Metamers
🟧 D. Positional isomers
✅ Correct: B. Ring–chain isomers
Reason: Same formula C₄H₈.
Q1️⃣3️⃣1️⃣ Which pair shows tautomeric isomerism?
🟦 A. Nitro ⇆ Aci-nitro
🟩 B. Ether ⇆ Alcohol
🟨 C. Aldehyde ⇆ Ketone
🟧 D. Alkene ⇆ Cycloalkane
✅ Correct: A. Nitro ⇆ aci-nitro
Reason: Proton shift + rearrangement.
Q1️⃣3️⃣2️⃣ How many stereoisomers are possible for 3-chloro-2-butanol?
🟦 A. 2
🟩 B. 3
🟨 C. 4
🟧 D. 1
✅ Correct: C. 4
Reason: Two chiral centers, no symmetry: 2² = 4.
Q1️⃣3️⃣3️⃣ Which isomerism results from different distributions of carbon atoms on either side of a functional group?
🟦 A. Chain
🟩 B. Metamerism
🟨 C. Position
🟧 D. Functional
✅ Correct: B. Metamerism
Reason: Seen in ethers, amines, esters.
Q1️⃣3️⃣4️⃣ Enantiomers differ in:
🟦 A. Debye moment
🟩 B. Rotation of plane-polarized light
🟨 C. Boiling point
🟧 D. Heat of combustion
✅ Correct: B. Optical rotation
Reason: Only property that changes.
Q1️⃣3️⃣5️⃣ Compounds with the same molecular formula but different carbon skeletons exhibit:
🟦 A. Functional isomerism
🟩 B. Chain isomerism
🟨 C. Position
🟧 D. Stereoisomerism
✅ Correct: B. Chain isomerism
Q1️⃣3️⃣6️⃣ Which of the following represents conformational enantiomers?
🟦 A. Gauche/anti butane
🟩 B. Staggered/eclipsed ethane
🟨 C. Orthosubstituted biphenyls
🟧 D. Cis/trans alkenes
✅ Correct: C. Orthosubstituted biphenyls
Reason: Restricted rotation “locks” chiral conformers.
Q1️⃣3️⃣7️⃣ How many chain isomers exist for C₆H₁₄?
🟦 A. 3
🟩 B. 4
🟨 C. 5
🟧 D. 6
✅ Correct: C. 5
Q1️⃣3️⃣8️⃣ cis-1-chloro-3-methylcyclohexane and trans-1-chloro-3-methylcyclohexane are:
🟦 A. Enantiomers
🟩 B. Diastereomers
🟨 C. Conformers
🟧 D. Identical
✅ Correct: B. Diastereomers
Q1️⃣3️⃣9️⃣ Substituted alkenes show E/Z isomerism when:
🟦 A. Both carbons have two identical groups
🟩 B. Only one carbon has different groups
🟨 C. Each carbon has two different groups
🟧 D. They are terminal alkenes
✅ Correct: C. Each carbon has two different groups
Q1️⃣4️⃣0️⃣ How many stereoisomers are possible for 1,2-dibromo-1,2-dichloroethene?
🟦 A. 2
🟩 B. 3
🟨 C. 4
🟧 D. 6
✅ Correct: C. 4
Reason: E/Z + enantiomerism for chiral configurations.
Q1️⃣4️⃣1️⃣ Which statement about meso compounds is FALSE?
🟦 A. They are achiral
🟩 B. They have an internal plane of symmetry
🟨 C. They rotate plane-polarized light
🟧 D. They contain stereocenters
✅ Correct: C. They rotate light
Reason: Meso compounds are optically inactive.
Q1️⃣4️⃣2️⃣ Which is NOT a requirement for optical activity?
🟦 A. Non-superimposability
🟩 B. Absence of symmetry plane
🟨 C. Chiral center (always)
🟧 D. Different substituents around center
✅ Correct: C. Chiral center (always)
Reason: Axial & planar chirality exist without chiral centers.
Q1️⃣4️⃣3️⃣ Which pair is NOT an example of structural isomers?
🟦 A. CH₃CH₂OH & CH₃OCH₃
🟩 B. Butane & isobutane
🟨 C. Propanal & propanone
🟧 D. Cis-2-butene & trans-2-butene
✅ Correct: D. Cis/trans are stereoisomers, not structural.
Q1️⃣4️⃣4️⃣ A molecule with 3 chiral centers but one internal symmetry plane will have how many stereoisomers?
🟦 A. 4
🟩 B. 6
🟨 C. 8
🟧 D. 3
✅ Correct: B. 6
Reason: Total 2³ = 8; symmetry eliminates 2 → 6.
Q1️⃣4️⃣5️⃣ Which isomerism is shown by ethanol and dimethyl ether?
🟦 A. Metamerism
🟩 B. Chain
🟨 C. Functional
🟧 D. Position
✅ Correct: C. Functional isomers
Q1️⃣4️⃣6️⃣ 1-chloropropane and 2-chloropropane are:
🟦 A. Chain isomers
🟩 B. Position isomers
🟨 C. Functional
🟧 D. Configurational
✅ Correct: B. Position isomers
Q1️⃣4️⃣7️⃣ Two molecules differ only by rotation around a single C–C bond. They are:
🟦 A. Conformers
🟩 B. Enantiomers
🟨 C. Functional
🟧 D. Tautomers
✅ Correct: A. Conformers
Q1️⃣4️⃣8️⃣ Which compound shows E/Z and chirality simultaneously?
🟦 A. 2-butene
🟩 B. 2-chloro-3-methylpent-2-ene
🟨 C. Ethene
🟧 D. Cyclohexane
✅ Correct: B. 2-chloro-3-methylpent-2-ene
Reason: Double bond (E/Z) + chiral carbon.
Q1️⃣4️⃣9️⃣ Which pair differs only in spatial arrangement but not in connectivity?
🟦 A. Enantiomers
🟩 B. Structural isomers
🟨 C. Metamers
🟧 D. Chain isomers
✅ Correct: A. Enantiomers
Q1️⃣5️⃣0️⃣ The most stable conformer of ethane is:
🟦 A. Eclipsed
🟩 B. Fully eclipsed
🟨 C. Staggered
🟧 D. Partially eclipsed
✅ Correct: C. Staggered
Reason: Minimum torsional strain.