Learn IUPAC nomenclature of organic compounds with simple rules and examples. Complete chapter-wise notes for Class 11 Chemistry 2025 syllabus, perfect for board exams and MDCAT/ECAT preparation."
Welcome to Learn Chemistry by Inam Jazbi! In this post, we will cover IUPAC nomenclature of organic compounds, an essential chapter of Class 11 Chemistry 2025 syllabus.
Here you’ll find simple rules, examples, and step-by-step explanations to easily name organic compounds. These notes are perfect for board exams, MDCAT, and ECAT preparation, helping students understand and memorize naming conventions quickly.
🧪 Quick Summary for MDCAT/ECAT/FSC:
IUPAC nomenclature is the systematic way of naming organic compounds based on their structure.
It ensures that each compound has a unique and universally accepted name.
🔥 Basic Steps to Name an Organic Compound:
Select the Longest Carbon Chain → It becomes the parent chain.
Number the Chain → Start from the end nearest to a functional group or substituent.
Identify Substituents → Name and position them using prefixes (like methyl, ethyl).
Identify Functional Group → Add the correct suffix (like –ol, –al, –one).
Combine Name → Prefix + Root + Suffix
👉 Example: CH₃CH₂OH → Ethanol
💡 Smart Tips:
✅ “Meth, Eth, Prop, But” → Remember first four roots.
✅ Functional group gets priority in numbering.
✅ Use commas for numbers, hyphens for letters.
✅ Alphabetical order for substituents.
✅ Practice naming with alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, aldehydes, and ketones.
⚡ Example Practice:
💥CH₃CH₂CH₃ → Propane
💥CH₃CH=CH₂ → Propene
💥CH₃CH₂CHO → Propanal
✨ Final Tip:
“Name from function, count from end — that’s how IUPAC rules blend!”
🔬 IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds: The Ultimate Guide for MDCAT/ECAT/FSC! 📚💡
IUPAC Rules for Organic Nomenclature
📘Basis of IUPAC System of Nomenclature
Order of Naming Organic Compounds
Prefix-Parent-Suffix;PPS
or
Locant-Prefix-Parent-Suffix; LPPS
🌟💥1. Root or Parent Hydrocarbon/Root word
(i) The continuous carbon chain (i.e. aliphatic hydrocarbon) is called Root or Parent Hydrocarbon.
(All aliphatic compounds are considered to be derived from this root hydrocarbon by the replacement of hydrogen atom(s) by alkyl or functional groups or the introduction of multiple bonds).
The Word root of IUPAC name indicates the number of carbon atoms in the longest possible continuous carbon chain chosen by a set of rules.
(ii)The shorter side chain outside the parent chain is called Alkyl Group.
(iii) The root chain is always enclosed in box.
(iv) The name of root chain is derived from the Greek (except the first four names) for the number of carbon atoms:
(v) The word roots used for different length of carbon chain (upto 100) are shown below.
🌟💥2. Suffixes
(i) A suffix is added to the root to indicate the presence of the principle substituent (principle functional group), in the molecule.
(ii) Each functional group (or a family) has a common suffix at the end of root names.
(iii) The suffix is again divided into two types i.e. primary and secondary.
(a) Primary suffix (immediately after the word root showing saturation or unsaturation)
(b) Secondary suffix (immediately after the primary suffix showing main functional group)
(a) Primary suffix
It is used to indicate the degree of saturation or unsaturation in the main chain. It is added immediately after the word root of IUPAC name.
(b) Secondary suffix
It is used to indicate the main functional group in the organic compound and is added immediately after the primary suffix in the IUPAC name.
Note
If there are two or more functional groups in a compound, the functional group with higher priority is to be selected as main functional group, which must be indicated by a secondary suffix. The remaining functional groups with lower priority are treated as substituents and are indicated by prefixes.
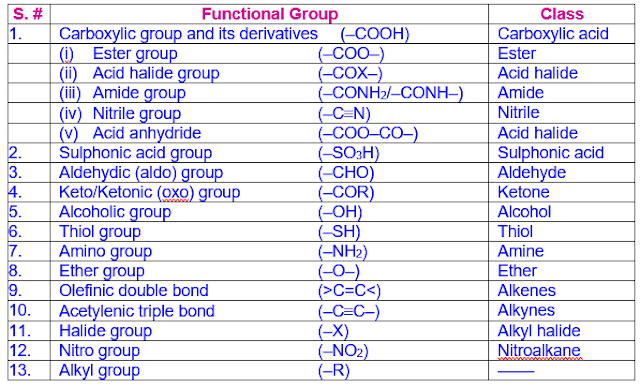
The suffixes as well as prefixes used for some important functional groups are shown in the following table in the decreasing order of their priority.
Also note that different suffix is used when carbon atom of the functional group is not part of the main chain.
Functional Group Suffixes and Prefixes
Note: Only the carbon atoms marked with asterisks, *C, are counted as part of root or parent chain.
Functional groups with more number of bonds with heteroatom are more preferred.
Nomenclature Priority Table (NPT)
🌟💥3. Prefixes
Prefixes are used to indicate the presence of alkyl or functional groups other than the principle group as well as their positions in the root chain. The prefix is used to indicate the side chains, substituents and low priority functional groups (which are considered as substituents). The prefix may precede the word root or the infix of IUPAC name.
The prefixes used for some common side chains and substituents are shown below
Remember that the alkyl groups along with halo, nitro and alkoxy have the same preference. They have lower priority than double and triple bonds.
🌟💥4) Infix
The infixes, like cyclo, spiro, bicyclo are added between the prefix(es) and root word in the IUPAC name to indicate the nature of parent chain. The infixes are sometimes called as primary prefixes.
💡 The "Cyclo" infix is used to indicate the cyclic nature of the parent chain.
💡 The "Spiro" infix is used to indicate the spiro compound.
💡The "Bicyclo" infix is used to indicate the bicyclic nature of the parent chain.
🧪📚Summary of Rules involved in writing IUPAC name of organic Compound
1. Firstly select the parent chain and assign a word root.
2. Next, the appropriate primary suffix(es) is added to the root word to indicate the saturation or unsaturation.
3. If the molecule contains functional group or groups, a secondary suffix must be added to indicate the main functional group. This is optional and not necessary if the molecule contains no functional group.
4. Prefix the root word with the infix "cyclo" if the parent chain is cyclic; or with the infix "spiro" if it is a spiro compound; or with the infix "bicyclo" if the compound is bicyclic.
5. Finally add prefix(es) to the IUPAC name, if there are side chains or substituents on the parent chain.
e.g.
The IUPAC name of the following compound (3-methylbutan-2-ol) is arrived in steps mentioned below.
Download here complete notes