Learn about Covalent Bond and its Types based on the number of shared electron pairs — single, double, and triple bonds. Perfect Chemistry notes for Class 9 and 11 students, covering concepts, examples, and diagrams for easy understanding.
🔸 Types of Covalent Bonds Based on the Number of Shared Electron Pairs
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration (usually an octet).
Depending on how many pairs of electrons are shared between atoms, covalent bonds are classified into three main types:
🧪 Table: Types of Covalent Bonds
| Type of Bond | Number of Shared Electron Pairs | Number of Bonds Formed | Example | Electron Dot Structure / Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Covalent Bond | 1 pair (2 electrons) | 1 | H₂, Cl₂, CH₄ | H–H, Cl–Cl, CH₄ |
| Double Covalent Bond | 2 pairs (4 electrons) | 2 | O₂, CO₂, C₂H₄ | O=O, O=C=O, H₂C=CH₂ |
| Triple Covalent Bond | 3 pairs (6 electrons) | 3 | N₂, C₂H₂ | N≡N, HC≡CH |
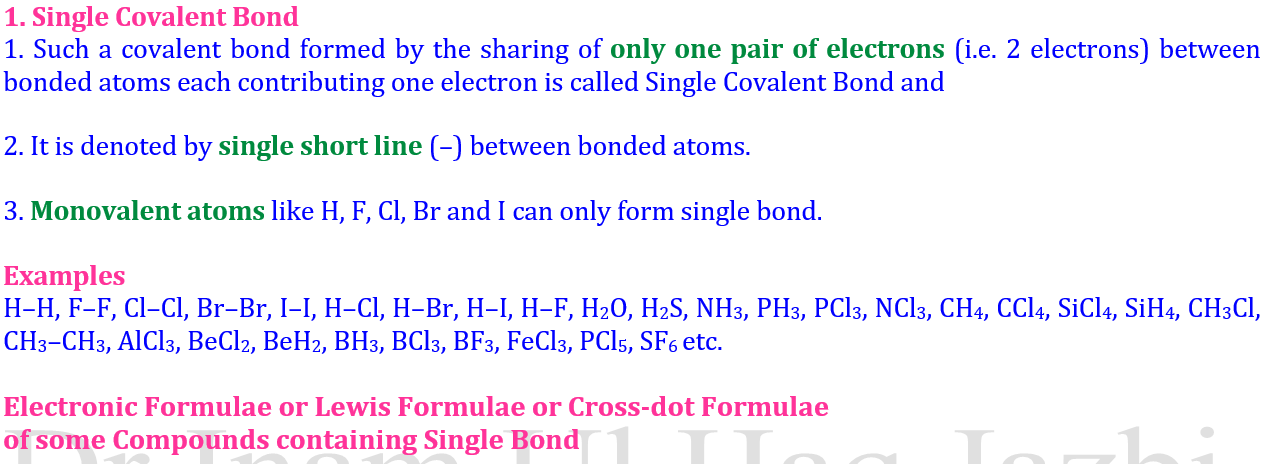
🔹 1. Single Covalent Bond
-
Involves one shared pair of electrons.
-
The bond is weakest and longest among the three.
-
Example:
-
Hydrogen molecule (H₂): Each H atom shares 1 electron.
-
Chlorine molecule (Cl₂): Each Cl atom shares 1 electron.
-
Representation: H–H, Cl–Cl
🔹 2. Double Covalent Bond
-
Involves two shared pairs of electrons.
-
The bond is stronger and shorter than a single bond.
-
Example:
-
Oxygen molecule (O₂): Each O atom shares two electrons.
-
Carbon dioxide (CO₂): Each C atom shares two pairs with two O atoms.
-
Representation: O=O, O=C=O
🔹 3. Triple Covalent Bond
-
Involves three shared pairs of electrons.
-
The bond is strongest and shortest among all.
-
Example:
-
Nitrogen molecule (N₂): Each N atom shares three electrons.
-
Acetylene (C₂H₂): Each carbon shares three pairs of electrons with another carbon atom.
-
Representation: N≡N, HC≡CH
🔹 Quick Summary
-
Single bond → Weakest, longest, 1 shared pair
-
Double bond → Medium strength and length, 2 shared pairs
-
Triple bond → Strongest, shortest, 3 shared pairs