Model Test Questions Chemistry Test # 9 for Chapter # 4 (Chemical Bonding)
Short Answer Questions
Q1. Draw dot and cross diagrams to show how
different types of chemical bonds are formed when fluorine reacts with
(a)
Hydrogen (b) potassium
Q2. What
is meant by octet and duplet rule?
Q3. Can
you draw an ion which is formed by the atom losing three electrons?
Q4. How
oxygen forms an anion?
Q5. What
is the difference between lone pair and bond pair?
Q6. Explain
why table salt has a very high melting point.
Q7. How
is electronegative value determined the formation of chemical bond?
Q8. Why is to easy for magnesium atom to lose
two electrons?
Q9. Atoms of metallic elements can form ionic
bond, but they are not very good to form covalent bonds. Why?
Q10. How
does an ion differ from an atom?
Q11. Describe dipole-dipole forces.
Q12. Write uses of adhesive material.
Q13.Why Intermolecular forces are weaker than
intra molecular forces?
Q14. Write
characteristics of metallic bond.
Q15. Covalent bonds are strong and hard to
break but why most of the covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
Q16. Write
down the characteristics of ionic compounds.
Q17. Why
ionic compounds are solid?
Q18. How
is hydrogen bonding affecting the physical properties of compounds?
Q19. Explain element attain stability?
Q20. Define metallic bond. How are metallic
bonds formed?
Long Answer Questions
Q1. Define ionic bond. Discuss the formation
of sodium chloride (NaCl).
Q2. What
is meant by covalent bond? Describe the formation of a covalent bond between
two nonmetallic atoms. Explain single, double and triple covalent bond with
examples.
Q3. How are electrons arranged in molecular
compound? Draw electron dot and cross structures or electronic formulae of H2,
O2, N2, CO2, HF, H2O, NH3,
C2H2, C2H4, C2H6,
and CH3Br.
Q4. What is coordinate covalent bond? Explain
with two examples.
Q5. What do you understand about ionic
character of covalent bond?
Q6. Differentiate the properties of polar and
non-polar compounds.
Q7. Explain the importance of glues and epoxy
resins in our society.
Q8. Give
difference between following:
(a) Ionic compounds and covalent compounds
(b) Polar and non-polar bond
(c) Covalent and co-ordinate bond.
(d)Ionic and covalent bond.
Q9. What is hydrogen bonding? What type of forces, either intramolecular
or intermolecular forces are present in hydrogen bond? Explain the origin of
hydrogen bonding?
Q10. Complete
the chart:
Answers of Short Answer Questions
Q1.Draw dot and cross diagrams to show how different types of chemical bonds are formed when fluorine reacts with
(a) Hydrogen (b) potassium
Answer
Q2. What is meant by octet and duplet rule?
Answer
In 1916 a
chemist G.N. Lewis used this fact, why atoms undergo chemical reactions. He
called his explanation as octet rule.,.
According to
Octet Rule:
“The outermost shell can have at maximum eight electrons and atoms
tend to acquire an outermost shell of eight i.e. atoms to acquire eight electrons in the valence shell is called the
octet rule.
According to
Duplet Rule:
Atoms to acquire two electrons in the valence shell is called
duplet rule.
Some atoms (like hydrogen, lithium, and beryllium) tend to attain
an outermost shell of only two electrons like the lightest noble gas helium.
This is in accordance with the general rule that all processes tend to move
towards the state of maximum stability.”
Q3. Can you draw an ion which is formed by the atom losing three electrons?
Answer
1. Aluminium metal
present in of IIIA group of the periodic table has ground state electronic configuration
of K2, L8, M3 (2, 8, 3)
2. Aluminium has 3 valence electrons.
3. It loses its all 3 valence electrons
attaining inert gas configuration of neon and change into aluminium cation (Al3+).
Al
(g) → Al3+ (g) + 3e–
2,8,3
(K2, L8, M3) 2,8 (K2, L8) [Ne]
Q4. How oxygen forms an anion?
Answer
Formation of Oxide ion i.e. O2– from Gaseous O
atom by the gain of two electrons)
1. Oxygen a non-metal
present in of VIA group of the periodic table, has electronic arrangement of K2, L6 (2, 6)
2. Oxygen
has 6 valence electrons and needs two electron to complete octet.
3. It
gains two electron attaining inert gas configuration of neon and change into
oxide ion O2– ion.
O(g) + 1e– →
O2– (g)
2,6
(K2, L6) 2,8 (K2, L8) [Ne]
Q5. What is the difference between lone pair and bond pair?
Answer
The main difference between bond pair
and lone pair is that bond pair is composed of two electrons that are in a bond
whereas lone pair is composed of two electrons that are not in a bond.
Q6. Explain why table salt has a very high melting point.
Answer
Sodium chloride is an example of ionic or electrovalent compound having strong ionic bonding in the form of strong electrostatic force of attraction between the oppositely charged sodium and chloride ions. Hence it requires more heat energy to overcome the strong electrostatic attraction between its positive and negative ions resulting in its high melting point.
Q7. How is electronegative value determined the formation of chemical bond?
Answer
The electronegativity values help to decide the nature of bond between two atoms.
1. If the difference in the electronegativities of bonded atoms is more than 1.7, then the bond is ionic.
2. If the difference in the electronegativities of bonded atoms is less than 1.7, then the bond is covalent
3. If the difference in electronegativities is zero or less than 0.5, then the bond is pure covalent or non-polar covalent bond. e.g. H–H, O=O, NºN, NCl3, CH4, F–F, Cl–Cl, I–I, Br–Br, etc.
4. If the difference in electronegativities is more than 0.5 but less than 1.7, then the bond is polar covalent or partially ionic in character e.g. H – F, H – Cl, H – O – H etc.).
If DE.N. > 1.7 –––– bond will be ionic.
If DE.N. < 1.7 –––– bond will be covalent.
If DE.N. > 0.5 < 1.7 –––– bond will be polar covalent or partially ionic.
If DE.N. = 0 or < 0.5 ––– bond will be non-polar or pure covalent.
Q8. Why is too easy for magnesium atom to lose two electrons?
Answer
Magnesium is an alkaline earth metal of group IIA. The IP of magnesium is less that helps it to lose its both valence electrons. In addition, loss of both electrons gives it noble gas electronic configuration of neon.
Q9. Atoms of metallic elements can form ionic bond, but they are not very good to form covalent bonds. Why?
Answer
Metallic elements are electropositive in nature. IP of atoms of metallic elements is low due to which they lose their valence electrons easily and hence form ionic bond. In addition, metals have few valence electrons usually less than 3 and hence acquiring noble gas configuration by sharing of electrons is not possible. Thus metals are not very good to form covalent bond.
Q10. How does an ion differ from an atom?
Answer
An ion is an electrically charged atom formed by the loss or gain of one or more electrons while an atom is a neutral particle. An ion usually has complete octet while an atom usually has incomplete octet. Thus ion is stable while atom is unstable.
Q11. Describe dipole-dipole forces.
Answer
Definition of Dipole-dipole forces
Dipole-dipole
forces exist between neutral polar unsymmetrical molecules.
Dipole-Dipole interactions result when
the two dipolar molecules interact with each other.
It is the electrostatic attractive
intermolecular force resulting from the interaction of the positive end of the
polar molecule with the negative end of the other polar molecule i.e. it is the
electrostatic attraction occurs between the oppositely charged regions of the dipolar
molecules.” DDI exists in SO2, SCl2,
PCl3, CH3Cl, HCHO, etc.
When
partially negative portion of one of the polar molecules is attracted to the
partially positive portion of the second polar molecule, the electrostatic
attraction is created between two molecules. These attractive forces are called
Dipole-Dipole interactions. DDF are generally weaker than hydrogen bond but
stronger than dispersion forces.
Example Dipole-Dipole Interaction
Dipole-dipole interaction can be seen in
hydrogen chloride. Chlorine atoms are much more electro negatives than hydrogen
atoms. A partial negative charge is created on Chlorine and in turn a partial
positive charge on hydrogen due to electronegative difference.
When two molecules of hydrogen chloride
come close to each other, the slightly negative end of one molecule is
attracted to the slightly positive end of another molecule. These attractive
forces are simply called dipole-dipole interaction as represented below:
Answer
Synthetic adhesives like epoxy resins
and glues are the substance that stick to the surface of the other objects.
Epoxy glue contains epoxy. Its form
strong bonds with glass, plastics, plywood, laminated boards and ceramic.
Another use for epoxy resin is the decorative flooring applications. Commonly,
epoxy resins are used where water resistance is required. Bridges, dams, power
stations are also coated with epoxy resins.
Explain how Aircrafts, cars, trucks and
boats parts are partially held together with epoxy adhesive
The excellent adhesive properties of
epoxy resins are due to the attractive forces between the epoxy resin and the
surface of the substrate. One of the most common uses of epoxy resin is for
adhesive purposes. For that purpose, epoxy resin is used in the construction of
vehicles, trucks, boats and aircrafts. Its drying time is 6-30 minutes hardly.
Answer
The intermolecular forces are weaker than intra molecular forces because these forces exist between either non-polar molecules or polar molecules which have weak charged particles and so they have weak attractive forces.
Answer
Definition
Metallic bonds are formed by the attraction between metal ions and
delocalized or "mobile" electrons. The electrostatic attractive forces between positive
nuclei of metal atoms and its electron sea/electron gas of delocalized valence
electrons which hold the metal atoms together is called metallic Bond.
Mechanism of Origin of metallic
Bond
1. Metal atoms
lose their valence electrons and change into positive ions or cations and
occupy a fixed position in a lattice.
2. The outer shell
valence electrons are free to move between the metals ions so are called
delocalized and move freely. In this way, electrons form a kind of negatively charged atmosphere called Electron Sea or Electron Gas in which
positive ions of metal are immersed.
3. Thus these free
valence electron of metal act as cohesive force holding metal atoms together
through metallic bond. Thus metallic bond involves the electrostatic attraction
between free-floating mobile valence electrons and the positively charged
closely packed metal ions.
Answer
Covalent compounds have generally low melting points because they
are made up of electrically neutral molecules having weak force of attraction in
the form intermolecular forces. Hence, only a small amount of
heat energy is required to break these weak intermolecular forces.
Q16. Write down the characteristics of ionic compounds.
Answer
Compounds having ionic bonds are called
ionic compounds. The properties of ionic compounds relate to how strongly the
positive and negative ions attract each other in an ionic bond.
The ionic compounds exhibit the following properties:
1. Physical State and Crystal Structure
Because of
strong binding forces, ionic compounds are always crystalline hard and rigid
solids at room temperature. Ionic compounds tend to be hard and brittle
Most of the ionic compounds are in a
solid or crystal form with strong electrostatic forces. In crystal structure of
sodium chloride each Na+ ion is surrounded by six Cl-
ions. Similarly, each Cl- ions is surrounded by six Na+
ions.
2. Non-Volatile in Nature
They are non-volatile in nature having high melting and boiling points because of the strong interionic binding forces in the form of electrostatic forces.
The large
attracting forces result in a very stable structure. Therefore a lot of energy
will be required to break these forces. So ionic compounds have high melting
points. For example, melting point of NaCl is 801ºC and boiling point 1413ºC.
3. Conductivity in molten or solution
state
Aqueous
solutions of ionic compounds also conduct electricity. This is because when an
ionic compound dissolves in water, the ions are free to move in aqueous
solution.
They do not
conduct electricity in the solid state as the ions are not free to move. But
they are good conductor of electricity in molten state or in solution form due
to free movement of the ions.
4. Solubility in polar Solvents
They are
soluble in polar solvents like water but insoluble in non-polar or organic
solvents of low dielectric constant such as oil, petrol, kerosene oil, benzene,
ether, carbon tetrachloride etc. as like dissolves like.
Q17. Why ionic compounds are solid?
Answer
Because of strong binding forces, ionic compounds are always crystalline hard and rigid solids at room temperature. Ionic compounds tend to be hard and brittle
Q18. How is hydrogen bonding affecting the physical properties of compounds?
Answer
Hydrogen bonding affects the physical properties of the molecules like melting and boiling point, density, solubility etc.
Q19. Explain element attain stability?
Answer
All the
atoms of different elements have the ability to make a bond with one
another. But why do atoms form chemical bonds? The essential answer is that
everyone in the world desires to be stable in their life. Atoms are just like
that, they are also trying to become more stable, so atom try to lose or gain
or share required number of electrons with each other to obtain the electronic
configurations of noble gases.
Answer
Definition of ionic
bond
The
electrostatic force of attraction arises due to complete transfer of one or
more valence electrons from one atom to another that binds oppositely charged
ions together is termed as ionic or Electrovalent Bond.
Formation of Ionic Bond in Sodium Chloride
In order to
form ionic bond, ∆E.N. between bonded atoms must be greater than 1.7.
The difference of E.N between Na and Cl is 2.1 (3-0.9). Thus sodium
metal and chlorine gas combine electrovalently or ionically to form formula
unit or crystal of an electrovalent compound, sodium chloride (NaCl). The
overall reaction can be shown as:
The
formation of ionic bond in sodium chloride involves the following steps:
Step I (Formation of Sodium ion i.e. Na+ from Gaseous Na
atom by the loss of an electron)
1. Sodium metal present
in of IA group of the periodic table has ground state electronic configuration of
K2, L8, M1 ( 2, 8, 1)
2. It has 1 valence
electron which it loses attaining inert gas electronic configuration of neon and
change into sodium cation (Na+).
Step II (Formation of Chloride ion i.e. Cl– from Gaseous Cl
atom by the gain of an electron)
1. Chlorine a non-metal
present in of VIIA group of the periodic table, has electronic arrangement of K2,
L8, M7(2, 8, 7.)
2. Chlorine
has 7 valence electrons and needs one
electron to complete octet. It
gains an electron lost by sodium attaining
inert gas configuration of argon and change into chloride ion Cl– ion.
Step III (Formation of Crystal
lattice by the Association of Na+ and Cl– ions)
the oppositely charged
ions i.e. Na+ and Cl– attract each other by electrostatic
force of attraction. Thus Na and Cl ions are joint by ionic bond and form
sodium chloride.
Na(g) → Na+(g) + 1e–
2,8,1 (K2, L8, M1) 2,8 (K2, L8) [Ne]
Cl(g) + 1e– → Cl– (g)
2,8,7 (K2, L8, M7) 2,8,8 (K2, L8, M8) [Ar]
Na1+(g) + Cl1–(g) → Na+ Cl– or Na+Cl–(s)
Answer
Definition
A covalent
bond is formed by mutual sharing of electrons between two atoms. In this type
of bond, electrons are not gained or lost by atoms. This type of bonding occurs
between two atoms of the same element or atoms of different elements. This
bonding occurs primarily between non-metals.
Covalent Bond Formation in hydrogen
Molecule
The
formation of covalent bond can be explained by considering the formation of
hydrogen molecule from hydrogen atoms. hydrogen
has one electron in its valence shell needs only one electron in order to
attain the stable noble gas configuration.
For the formation of covalent bond, two
hydrogen atoms share their valence electrons, each hydrogen atom, contributes
one electron. both atoms achieve
the electronic configuration of noble gas helium and satisfy the duplet rule.
The electrons of atoms that pair up to form a chemical bond are called bond
pair electrons. A covalent bond is generally represented by a short straight
line (–) between two bonded atoms.
1. Single Covalent Bond
A covalent
bond which is formed by the mutual sharing of one bond pair is called a single
covalent bond. Mutual sharing of two electrons between two atoms form a single
covalent bond. H–H, F–F, Cl–Cl, Br–Br, I–I, H–Cl, H–Br, H–I, H–F, H2O,
H2S, NH3, PH3, PCl3, NCl3,
CH4, CCl4, CH3Cl, CH3–CH3,
AlCl3, BCl3, BF3, FeCl3 etc. It is denoted by single short line (–) between bonded atoms.
Examples
2. Double Covalent Bond
A covalent bond which is formed by the
mutual sharing of two bond pairs called a double covalent bond. Mutual sharing
of four electrons between two atoms form a double covalent bond. It is
represented by two short line (=)
between bonded atoms e.g. O=O, O=C=O (CO2), H2C=CH2
(C2H4), S=C=S (CS2), SO2, SO3,
NO2.
Formation of Oxygen Molecule
Oxygen atom belongs to group VIA of the
periodic table and it has 6 valence electrons in its outer shell. It needs two
more electrons to achieve a stable octet electronic configuration. Each oxygen
atom will share two of its outer electrons with another oxygen atom to form an
oxygen molecule (O2). Thus, two pair of electrons are shared between
the two oxygen atoms to form a double covalent bond.
3. Triple Covalent Bond
A covalent bond which is formed by the
mutual sharing of three bond pairs is called a triple covalent bond. Mutual
sharing of six electrons between two atoms form a triple covalent bond. It is
denoted by three short lines (º) between
bonded atoms. e.g. nitrogen; NºN (N2), ethyne; HCºCH (C2H2), H–CºN (HCN).
Formation of Nitrogen Molecule
Nitrogen is a non-metal. Each nitrogen
atom has five electrons in its outer shells. Two nitrogen atoms will share
three electrons to form three covalent bonds which is called triple covalent
bond and formed a nitrogen molecules (N2).
Q3. How are electrons arranged in molecular compound? Draw electron dot and cross structures or electronic formulae of H2, O2, N2, CO2, HF, H2O, NH3, C2H2, C2H4, C2H6, and CH3Br.
Q4. What is coordinate covalent bond? Explain with two examples.
Answer
Definition and Representation
It is a
special type of covalent bond which is proposed by Sidgwick who named it as Dative Bond.
The type of bond in which bond pair of
electrons is contributed by one atom only, is called coordinate covalent or
dative covalent bond.
Examples
1.Formation of Ammonium Chloride by the
Reaction between Ammonia and Hydrogen Chloride
The reaction between ammonia and
hydrogen chloride involves the formation of a dative bond between N atom in NH3
containing lone pairs and H+ ion from HCl. When ammonia reacts with
hydrogen ions (H+) in an aqueous solution of an acid, the hydrogen
ion is attracted to the lone pair and a coordinate covalent bond is formed.
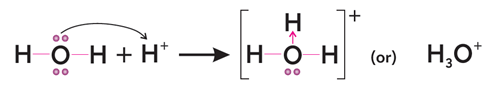
2. Formation of Oxonium/Hydronium Ion
In the formation of oxonium or hydronium ion (H3O+)
from water molecule and hydrogen ion or proton, H+ (released by acid
like HCl in aqueous solution), the oxygen atom of water donates its lone pair
to hydrogen ion, H+ for one-sided sharing to make co-ordinate
covalent bond.
Q6. Differentiate the properties of polar and non-polar compounds.
Answer
Polar and non-polar both compounds differ in properties.
(i) Nonpolar
covalent compounds are generally insoluble in water while polar covalent
compounds are soluble in water.
(ii) Non-polar
covalent compounds do not conduct electricity in the solid, molten or aqueous
solution, but polar covalent compounds
usually conduct electricity due to the formation of ions with water.
(iii) Non-polar
covalent compounds are soluble in non-polar solvent like petrol, benzene etc.
While polar covalent compounds
insoluble in non-polar solvent.
(iv) Few
examples of polar covalent compounds are H2SO4, H2O,
HCl, HF, HBr, HI
(v) Few
examples of non-polar covalent compounds are CO, CH4, C2H6.
Q8. Give difference between following:
(a) Ionic compounds and covalent compounds
(b) Polar and
non-polar bond
(c) Covalent and co-ordinate bond.
(d) Ionic and covalent bond.
Answer
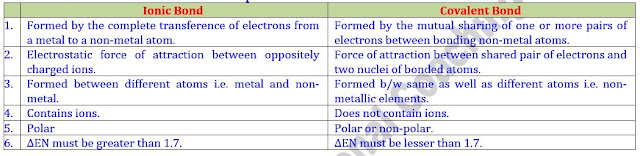
Difference between Ionic, Covalent and Dative Bond
Distinction between Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Distinction between Ionic and Covalent Compounds
Difference between Polar and Non-Polar Bonds
Q9. What is hydrogen bonding? What type of forces, either intramolecular or intermolecular forces are present in hydrogen bond? Explain the origin of hydrogen bonding?
Answer
Definition of hydrogen bond
The interaction between partially positive charged hydrogen atom of
one molecule with electronegative atom of other molecule is called Hydrogen Bond or
Protonic Bridge. Hydrogen bond is denoted by dotted lines
(- - - -).”
Nature of hydrogen bond
It is the intermolecular partially electrostatic dipole-dipole attractive
force (that exists between positively charged hydrogen atom bonded to highly
electronegative non-metallic atoms such as F, Cl, O, S and N in a polar bond
and a lone pair of electrons on an adjacent small electronegative atom like F,
O or N). Hydrogen bond is an unexceptionally
(unusually) strong and special type of dipole-dipole interaction.
Explanation
In molecules containing N–H, O–H or F–H
bonds, the large difference in electronegativity between the H atom and the N,
O or F atom leads to a highly polar covalent bond. Because of the difference in
electronegativity, the H atom bears a partial positive charge (δ+)
and the N, O or F atom bears a partial negative charge (δ-). The
high partial positive charge on H atom enables to attract highly
electronegative (N, O, or F) atom of the other molecule.
Example of
HB
Consider the example of hydrogen fluoride. The fluorine atom is more electronegative. They tend to pull on the shared pair of electrons, creating a partial negative charge on itself and a partial positive charge on the hydrogen. The partial positive charge bearing hydrogen, then forms a bond with the electronegative atom of a neighboring molecule, while its electronegative element forms another bond with the positive hydrogen of another neighboring molecule. Therefore, several molecules combine by hydrogen bonding. This type of strong attractive force involving hydrogen and causes the association of molecules in larger clusters as (HF)x, (H2O)x, (NH3)x is known as Hydrogen Bond.