2.Which one is the strongest acid among following options?
(a) FCH2COOH
(b) Cl2CH2COOH
(c) ClCH2COOH
(d) F2CH2COOH
(b) Dipole-dipole attraction
(c) Hydrogen bonding
(d) debye force
Explanation
4. The organic reaction which proceeds through heterolytic bond cleavage are called
(a) Ionic
(b) Polar
(c) Non-polar
(d) both (a) and (b)
Explanation; (d)
(a) BF3
Explanation; (Answer; b)
The negatively charged carbon atom in Methyl carbanion (CH3−)
is sp3 hybridized , with three bond pairs and one lone
pair of electrons, giving it to pyramidal (distorted tetrahedral) shape same is
that of NH3.
6. Metamers of ethyl
propionate are
(a) C4H9COOH and HCOOC4H9
(b) C4H9COOH and CH3COOC3H7
(c) CH3COOCH3 and CH3COOC3H7
(d) CH3COOC3H7
and C3H7COOCH3
Explanation; (Answer; d)
Metamers have different type of alkyl group around polyvalent functional group. In option d, ester group (-COO-) is linked with different number of carbons on its either side.
7. Isomers of propionic
acid are
(a)HCOOC2H5 and CH3COOCH3
(b) HCOOCC2H5 and C3H7COOH
(c) CH3COOCH3 and C3H7OH
(d) C3H7OH
and CH3COOCH3
Explanation;
(Answer; a)
Propionic acid is
isomeric with 3 C ester which has two metamers.
8. For which of the following parameters the structural isomers C2H5OH and CH3OCH3 would be expected to have the same values? (assume ideal behaviour)
(a) Gaseous densities at the same T and P
(b) Vapour pressure at the same temperature
(c) Heat of vapourization
(d) Boiling points
Explanation;
(Answer; a)
Since the molecular weight of C2H5OH & CH3OCH3 are
same so in its vapour phase at same temperature & pressure the densities
will be same.
Vapour
density = (Molecular weight)/2. As both the compounds have same molecular
weights, both will have the same vapour density. Hence, gaseous density of both
ethanol and dimethyl ether would be same under identical conditions of
temperature and pressure. The rest of these three properties; vapour pressure,
boiling point and heat of vaporization will differ as ethanol has hydrogen
bonding whereas ether does not.
Explanation; (Answer; a)
In 3,4-dimethylheptane there are 4 primary, 3 secondary and 2 tertiary carbons. It has no quaternary carbon
13. The compounds CH3CH=CHCH3
and CH3CH2CH=CH2
(a) contain same of sp3-sp3, sp3-sp2 and sp2-sp2 C-C bonds
(b) exist together in dynamic equilibrium
(c) are position isomers
(d) are tautomers
Explanation;
(Answer; c)
Both compounds differ in the position of double bond so they are position isomers.
14. Which of the
following carbocation is least stable?
(a) tert-alkyl
(b)sec-alkyl
(c) pri-alkyl
(d)
methyl
Explanation;
(Answer; d)
15. Benzoic acid when treated with PCl5, the product
is:
(a) Benzoyl chloride
(b) Benzoyl amide
(c) Benzoyl anhydride
(d) None of them
Explanation; (Answer; a)
16. Which class of compounds shows H-bonding even more than in
alcohols?
(a) Phenols
(b) Carboxylic acid
(c) Aldehydes
(d) Ethers
Explanation;
(Answer; b)
Forms H-bonding be means of two highly electronegative atoms
present in it
17. In CH3COOH and HCOOH, HCOOH will be which of the
following
(b)More acidic
(b)Less acidic
(b)Equally acidic
(b)None of them
Explanation;
(Answer; a)
Presence of methyl group decreases the acidic character of acetic acid due to positive inductive effect (+I)
18. The total number of isomers for C4H8 is
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) 8
Explanation; (Answer; b)
Five constitutional isomers are possible with C4H8.
The five constitutional isomers include:1) But-1-ene
2) But-2-ene
3) 2-Methylpropene
4) Cyclobutane
5) Methylcyclopropane

But-2-ene exists as two geometrical
isomers namely cis and trans
Hence total isomers with this molecular formula are 6.
22. Phenylmagnesium bromide reacts with solid dry ice followed by acid-hydrolysis to form
(a) Bromobenzene
23. Which acid of the following is not a fatty acid?
23. In the following reaction, the product R is
Explanation; (Answer; b)
26. Which of the following reacts immediately with conc HCl in the presence of Zinc Chloride?
(a) Primary Alcohol
(b) Secondary Alcohol
(c) Tertiary Alcohol
(d) Ether
The reagent, a mixture of conc. HCl and anhydrous ZnCl2 is called Lucas reagent, which is used to distinguish between 1o, 2o and 3o alcohols. The test is called Lucas test.
Note: Lucas reagent is required for primary and secondary
alcohol only.
Primary alcohols react with Lucas reagent very slowly on
heating to give alkyl chlorides.
Secondary alcohols react with Lucas reagent much faster.
Tertiary alcohols instantaneously react with HCl at room temperature.
3o alcohol
+ Lucas reagent → Immediate turbidity (cloudiness).
2o alcohol
+ Lucas reagent → Turbidity (cloudiness) after 5 minutes.
1o alcohol
+ Lucas reagent → No reaction or cloudiness appears on heating
27. The percentage of s-character of the hybrid orbitals in ethane, ethene and ethyne are respectively:
(a) 50, 75, 100
28. Which of the
following have incorrect molecular formula?
(I) Icosane – C10H22
(II) Triacontane – C30H62
(III) Nonane – C9H20
(IV) Dodecane – C12H24
(a) I and IV
(b) IV only
(c) II and IV
(d) II only
Dodecane – C12H26
(being an alkane
follows general formula CnH2n+2
29. The compound
which has one isopropyl group is
(a) 2,2,3,3-tetramethylpentane
(b) 2,2,-diemthylpentane
(c) 2,2,3-trimehtylpentane
(d) 2-methylpentane
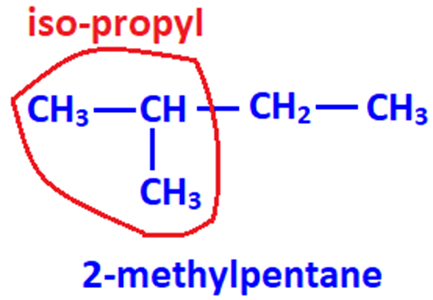
2-methylalkanes always have isopropyl group at the end of chain.
(a) Kolbe’s reaction
31. Decreasing order of C – C bond length in following compounds is
(I) C2H4 (II) C2H2 (III) C6H6 (IV) C2H6
(a) IV > III > I > II
(b) I >II >IV > III
(c) II > I > IV > III
(d) IV > I > III > II
Decreasing order of C – C bond length follows the order
Alkane > Benzene > Alkene > Alkyne
32.
(a) 1-nitrochlorobenzene
(b) 3-nitrochlorobenzene
(c) 4-nitrochlorobenzene
(d) 1,2-dinitrochlorobenzene
Nitration of benzene gives nitrobenzene which on chlorination forms meta-nitrochlorobenzene as nitro group is meta directing group.
33. Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding the reaction between Cl2 and C2H6?
(a) It is a substitution reaction and the reaction mechanism involves free radicals
(b) The reaction will give a single product of C2H5Cl.
(c). The first step in the mechanism is the cleavage of the Cl-Cl bond to give chlorine atoms
(d) The reaction can be initiated with either sunlight or heat.
34. Which of the following compounds will not show geometrical isomerism?
(a) 3-Phenyl-2-propenoic acid
The given compound has only one -COOH group. Hence it requires only 1 mole of NaOH.
36. Which one of the following compounds will show geometrical isomerism?
Two methyl groups on the same side form the cis isomers – cis-2-butene
Two methyl groups on the opposite sides form the trans isomers – trans-2-butene


In 1-butene, cis and trans forms do not exist because two H atoms are attached to the same carbon atom. Hence 1-butene does not exhibit geometrical isomerism.

(a) 5